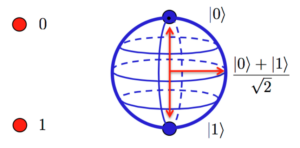
Developing the hardware for quantum computing and hybrid quantum/classical computing systems is only one step in developing practical quantum computing solutions. Development of quantum algorithms and related software programming of the qubits is required to implement practical applications using quantum approaches to computing. Earlier FAQs in this series looked at the Basics of quantum computing, […]
Merging quantum and classical computing in a hybrid system
Practical quantum computing requires connections to the outside world. Those connections may be for collaboration between a quantum computer and an external computing resource such as a supercomputer. They can simply output the results of the quantum computations in a manner accessible and usable by human operators. In either case, there’s a paradox between the […]
Quantum computing system architectures
There are a variety of possible physical embodiments of quantum computers. This FAQ will explore several of those possibilities. Qubits, Hamiltonians, and decoherence are three important concepts needed when discussing various approaches to quantum computing. Check out the first FAQ in this series for a more detailed discussion of “What are the basics of quantum […]
What are the basics of quantum computing?
The concept of quantum computing has been around since the early 1980s when physicist Paul Benioff proposed a quantum mechanical model of the Turing machine. Benioff’s ideas were built upon by Richard Feynman, Yuri Manin, and others. He suggested that a quantum computer had the potential to simulate things that can’t be done using classical […]
Mioty LPWAN – what’s it good for?
Mioty (pronounced “My IoT”) is targeting a wide range of potential application spaces for its low power wide area network (LPWAN) technology. In several cases, it’s intending to supplement or even supplant existing protocols such as WiFi and LoRa, even Ethernet. Mioty is a standardized software-based massive IoT connectivity solution operating in the license-free spectrum. […]
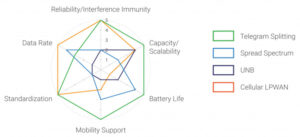
How does mioty compare with other flavors of LPWAN?
Mioty (pronounced “My IoT”) offers designers of low power wide area network (LPWAN) devices and networks another set of performance tradeoffs. This FAQ will start with an overview of four examples of technical approaches to ultra-narrowband (UNB) transmission interfaces, including: triple diversity UNB (3D-UNB), telegram splitting UNB (TS-UNB), dynamic download UNB (DD-UNB), and Lfour. It […]
What is mioty telegram splitting LPWAN?
Mioty (pronounced “My IoT”) is the latest contender in the increasing-crowded field of low power wide area network (LPWAN) offerings. According to the mioty website: “With its best-in-class reliability and scalability, mioty is designed for massive industrial and commercial IoT deployments.” Quite a goal. But with founders including Texas Instruments, Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits […]
How does RISC-V fit into automotive systems?
RISC-V is being used in a surprising range of automotive systems ranging from ASIL-D safety rated controllers and security co-processors, artificial intelligence (AI) accelerators, controllers for advanced electric vehicle (EV) battery chargers based on gallium-nitride (GaN) power semiconductors, and even in high-voltage monolithic motor drive controllers for light EVs. The following is a sampling of […]
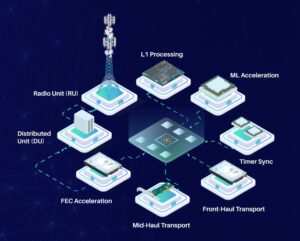
What’s the future for RISC-V in 5G?
The versatility of the RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA) can be seen in the breadth of 5G applications using the technology. Examples include a complete 5G base station system-on-chip (SoC), a 5G small cell distributed unit (DU) SoC, a recurrent neural network (RNN) IC optimized for 5G radio resource management, even handsets are under development […]
Domain specific accelerators for RISC-V
Domain specific accelerators (DSAs) are specialized hardware computing engines optimized for specific tasks. DSAs have been developed for graphics, simulation, image processing, deep learning, bioinformatics, and other tasks. Compared to general purpose processors, accelerators offer orders of magnitude improvements in performance/cost and/or performance/watt. The previous FAQ in this series, “What’s the future for RISC-V in […]