Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) is a type or category of the processor, or Instruction Set Architecture (ISA). Speaking broadly, an ISA is a medium whereby a processor communicates with the human programmer (although there are several other formally identified layers in between the processor and the programmer). An instruction is a command given to […]
FAQ
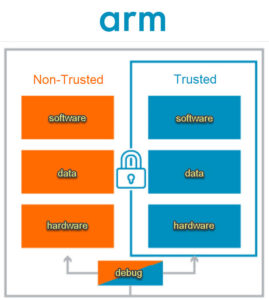
Arm TrustZone explained
Arm TrustZone is a system-wide approach to embedded security option for the ARM Cortex-based processor systems. Cortex-based cores are used in everything from microcontrollers (MCUs) to high-performance processors. Arm TrustZone is an embedded security technology that starts at the hardware level by creating two environments that can run simultaneously on a single core: a secure […]
Making sense of displays: OLED, AMOLED, POLED, PMOLED and T-OLED
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) displays are made using organic light emitting diodes, which emit light when current runs through them. The basic colors of light for these diodes are Red, Green, and Blue (RGB), which combine to create an extensive range of colors of visible light. OLED displays are different from Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) […]
Asynchronous serial communication explained (including TTL, UART, and RS232)
A microcontroller can communicate with a computer or another device by using a standard method of communication that has been worked out ahead of time. Serial communication is a very common means of communication. Unless you’ve been working in electronics for a while, you might not have a full handle on the plain facts about […]
NOR flash and NAND flash memory usage trends are evolving
Not everyone is familiar with the jargon that experienced engineers and technicians use when they talk about Microcontrollers (MCUs) and memory. NAND and NOR flash memories are used both externally and integrated with MCUs onto System-on-Chips (SoCs) and memory usage trends are evolving around other changes in technology. Both NOR and NAND flash have a […]
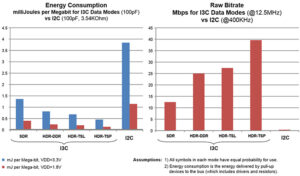
The improved inter-integrated circuit (I3C)
A new successor to the Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C or I2C) bus communication interface is under development, hosted by the Sensor Working Group at the MIPI Alliance. The Improved Inter-Integrated Circuit, I3C, (pronounced “Eye-three-See”) is backward compatible with I2C but will be better suited for handling an abundance of sensors. The I3C specification was released in […]
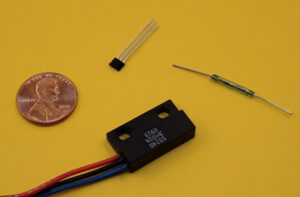
Magnetic Reed switch: an amazing addition to your design toolbox
Reed switches are simple, passive, electromechanical components that were invented circa the 1940s. Reed switches aren’t mentioned much in electronic literature or forums that much, but they have some amazing capabilities. Reed switches are sometimes called magnetic switches. Reed switches open or close when exposed to a magnetic field. The reed switch consists of a […]
Driving high-wattage output with a solid-state relay
Microcontrollers are designed to handle only low voltage and current signals on their input and outputs. So how does one control and drive a high wattage load such as an electric heater using an MCU? One of the easiest and most efficient ways is to use a Solid-State Relay (SSR). An SSR allows you to […]
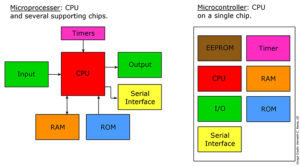
Microcontrollers vs. Microprocessors: What’s the difference?
Microcontrollers (MCUs) tend to be less expensive than, simpler to set-up, and simpler to operate than microprocessors (MPUs). An MCU can be viewed as a single-chip computer, whereas an MPU has surrounding chips that support various functions like memory, interfaces, and I/O. The MCU vs. MPU question may seem simple, but there are some prominent […]
Gold or Tin Contacts? Just don’t mate them together
You might know that gold is a noble metal, whose electron shells are completely filled and unlikely to be attracted to other elements. You might know that old contacts provoke less signal noise than other metals, but did you know that contacting tin with gold will corrode the gold over time? Mixing tin contacts with […]