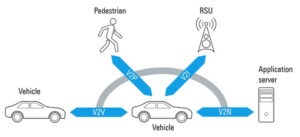
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication includes vehicle-to-network (V2N), vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I), vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), vehicle-to-cloud (V2C), vehicle-to-pedestrian (V2P), vehicle to device (V2D), and vehicle to grid (V2G). This FAQ begins with a review of dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) and cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X) technologies for V2X communications, looks at the four V2X service types and the structure of telematics control […]
FAQ
What are the five levels of vehicle connectivity?
There are several efforts underway to define levels of vehicle connectivity that parallel the levels of driving automation defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). The concept of autonomous vehicles, particularly at the higher levels of automation like self-driving cars, is still largely aspirational and a goal for some time in the future. Connectivity, […]
What’s different about MCUs for use in vehicle networking?
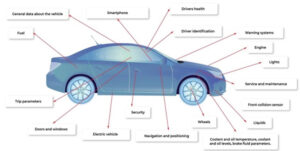
The increasing use of automated driving functions, more sensors and actuators, and growing V2X connectivity is increasing the challenges related to vehicle electric/electronic (E/E) architectures and in-vehicle networking (IVN). This FAQ will review the performance requirements for microcontrollers (MCUs) needed to support time-sensitive networking (TSN) in IVNs, move over to look at service-oriented gateways, domain […]
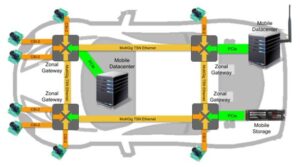
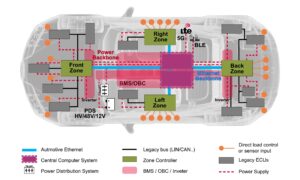
Zonal E/E will transform automotive architectures
The transition from numerous ECUs to zones will occur over several years from roughly 2025 to 2030. Each OEM will use its own architecture. Long before the smartphone, the number of interconnected electronics and electrical equipment on automobiles, especially high-end vehicles, led pundits to describe a car as a computer on wheels or a digital […]
What is TinyML?
Data science has not just remained a field of scientific computing and research. In the internet-connected world, data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence are far more applicable than ever imagined. No doubt, the very first leap in the practical applications of machine learning and artificial intelligence happened when enterprise websites, including social media platforms, e-commerce […]
What are top applications of CAN protocol?
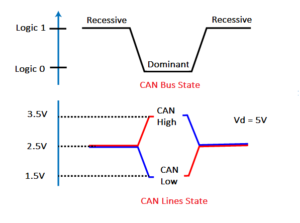
The CAN (controller area network) protocol was developed by the European automotive electronics company Robert Bosch GmbH in 1983 for in-vehicle networks. The intention behind the development of the CAN protocol was to enable robust data communication between different electronic control units (ECU) and microcontroller control units (MCU) of a vehicle on a single wire […]
What are the top tools for developing embedded software?
The embedded software or firmware is the brain of an embedded device. This type of software, however, works differently than conventional forms found on PCs or mobile devices — these are generic and work identically on such operating systems. PC software runs without directly accessing the underlying hardware. The purpose of embedded software works alternatively […]
What is MicroPython?
MicroPython implements the Python 3 programming language for microcontrollers and microcomputers. It is a firmware solution designed to implement the high-level language features of Python into low-level hardware platforms. The firmware is optimized to run in constrained environments while allowing a small subset of Python 3 standard libraries into embedded programming. MicroPython firmware can run […]
The top computer vision tools for embedded systems
Computer vision is reaching new levels, far beyond basic image processing. This is thanks to the integration of artificial intelligence. AI now enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images that can be used in advanced industries. Currently, one of the most common applications is in security and surveillance. A computer vision […]
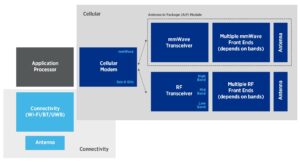
5G mmWave test builds on RF best practices
The high level of integration in today’s mmWave phone means traditional test methods no longer apply.