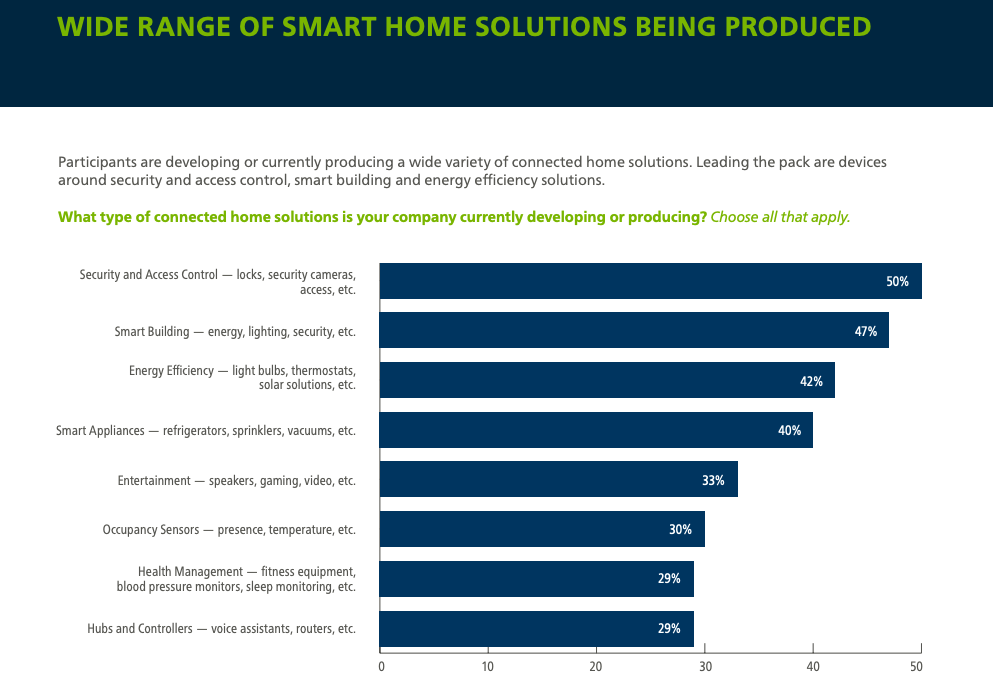
According to MarketsandMarkets, a marketing research firm, worldwide smart home market revenue will reach $135 billion by 2025. The driving force behind this revenue climb is expanding sectors, including the IoT, home automation, and smart appliances.
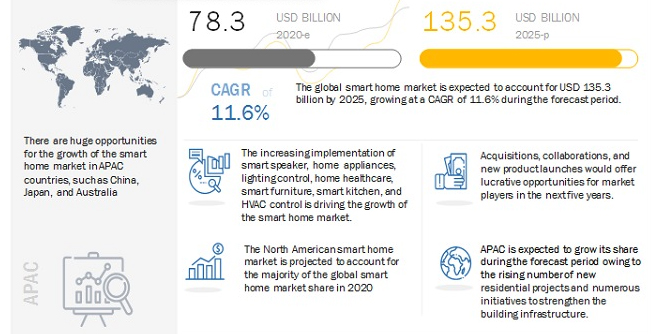
As shown in the diagram (part of a report produced by Jabil and Dimensional Research), the top smart home applications include security management, smart buildings, energy efficiency management, smart appliances, and entertainment.
What is the smart home market all about? What are the requirements to succeed in this market segment? The following are the questions that developers commonly ask:
What is smart home technology?
A smart home is a connected home that uses wireless smart devices to provide day-in and day-out convenience. The modernization these devices can bring about helps to improve the quality of life. Typically, these devices are cloud-based with built-in artificial intelligence (AI) controllable by voice or smartphone.
Smart devices vary from simple to sophisticated. That variety encompasses everything from turning off a light with a voice command to appliances advanced enough to talk to users. The potential of future smart home devices is tremendous and limited only by one’s imagination. One example is a refrigerator that is equipped with an internal camera, computer, and wireless connection. Peering into the fridge to know which groceries need ordering can happen via smartphone. Or a slow cooker can be accessed remotely, so dinner will be ready to eat at a specified time. In short, this automation will add to the quality of life while saving time and reducing stress. Energy- and money-saving home temperature and landscape watering control, aided by smart devices’ weather sensing ability, is another plus.
Smart home applications are very broad, but most applications can be classified as belonging to one of the following categories. Smart home devices’ most noticeable applications are the “Hi, Alexa” and “Hi Google” voice control systems. But other applications are not as obvious, such as security and energy management.
- Home automation
- Smart home entertainment
- Safety and security
- Environmental control and energy management
What smart home devices are available today?
There are many different types of smart devices available today, shown below. More are being added to the list. Note that some vendors may classify products such as automatic vacuum cleaners as smart home devices. However, the more accepted definition is: “connected or managed devices that may do more than one thing.”
- Smart door locks can be turned on and off remotely, using code or biometrics such as fingerprints and facial recognition.
- Smart doorbells equipped with a video camera allow residents to see who is at the door. Some devices can automatically record a video clip for security reasons.
- Surveillance systems with HD video cameras can monitor activities inside and outside the house and be viewed remotely from a smartphone.
- Smart lighting can be turned on and off from a smartphone or via voice control. Some smart lighting solutions can respond to ambient light by turning it on or off.
- Smart sprinklers can be controlled or programmed remotely. Sensors even enable some smart sprinklers to shut off when rain is detected or flooded due to sprinkler damage.
- Smart appliances belong to a broad category, including cookers, dishwashers, washing machines, dryers, and refrigerators. These appliances can be monitored and controlled remotely, as well as accept audio commands.
- Smart thermostat sensors can detect temperature, humidity, and human presence, then automatically adjust the temperature to reduce energy use.
- Garage doors can be monitored and controlled remotely from anywhere using a cell phone.
- For safety, smart devices are available to detect fire, smoke, and carbon monoxide and water leaks and freezing temperatures, to protect pipes or agricultural products, for example.
- Smart devices are available to detect motion, glass breakage, and intrusion through forced entry to provide security.
- Other ideas such as remote-control lawnmowers and automatic pet feeders so pets will not go hungry even when nobody is home to feed them. Automatic houseplant watering is trying to make it to the smart home appliance list.
What wireless protocols are used in the smart home?
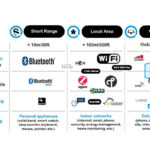
Through the years, various smart home protocols have been implemented. They include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Z-Wave, Zigbee, LTE, Insteon, X10, Universal Powerline Bus (UPB), Thread, WeMo, and other proprietary technologies. Today, the two leading smart home wireless protocols are Z-Wave and Zigbee.




Oh my God! Thank you so much for talking about the existence of smart thermostat sensors which can be very useful during winter and summer. My niece has been thinking of upgrading the entirety of her house next year. I think it’s better for her to consult a professional beforehand so she’ll make the right installation later.