Part 1 focused on HaLow technology; this part will explore who the major players are and discuss the future of the technology.
Who are the major HaLow players?
A few silicon startups are taking the lead in Wi-Fi HaLow rather than the traditional major chipmakers. They include Morse Micro, Newracom, Methods2Business (an IP provider), and Palma Ceia SemiDesign (PCS). Companies providing Wi-Fi Halow modules include Morse Micro, Silex Technology, and Alfa Network.
How secure is HaLow?
Wi-Fi HaLow uses the WPA3 and Wi-Fi Enhanced Open security standards. Over the years, the Wi-Fi Alliance has offered four different security protocols.
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
- Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2)
- Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3)
WPA3 is the most current version and improves upon the previous versions. These improvements include stronger password protection for enterprise networks. Also included is individualized encryption for personal and open networks and support for over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates.
Based on opportunistic wireless encryption (OWE), the Wi-Fi Enhanced Open standard provides encryption and privacy for non-password-protected networks in hotels, restaurants, and other public areas. Note that it does not provide authentication.
How does HaLow compare with other LPWAN solutions?
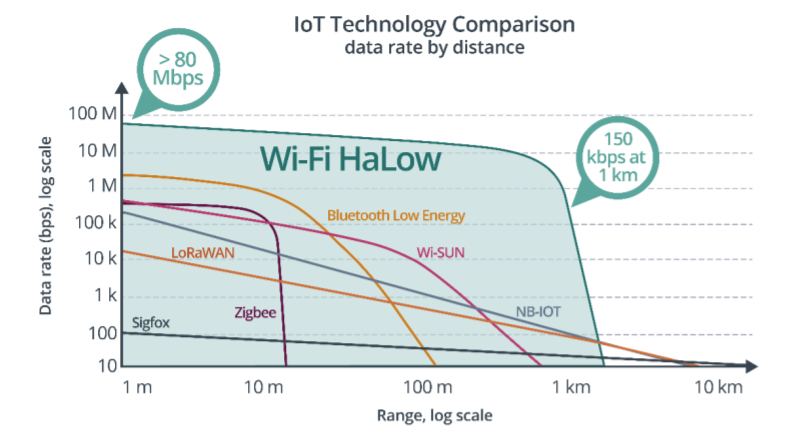
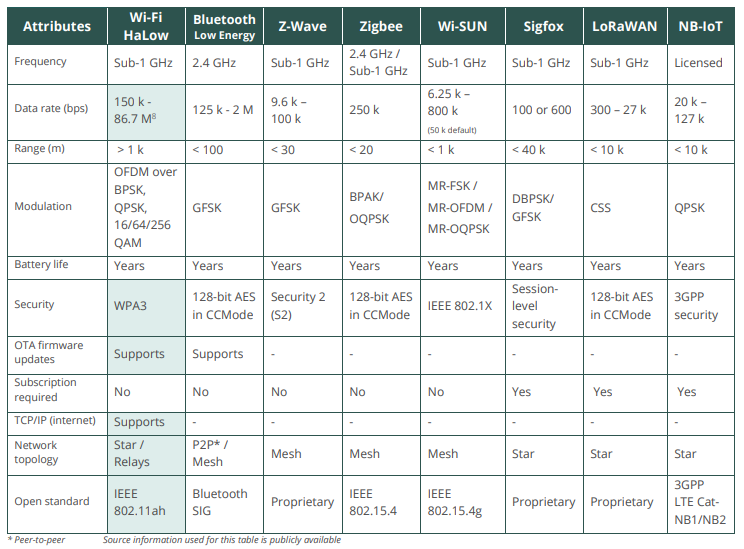
Figures 4 and 5 compare HaLow with other leading LPWANs. HaLow is offering the highest data rate among all the LPWAN technologies. The Wi-SUN FAN 2.0 has upgraded the data rate speed to 2 Mbps, missing from the chart published.
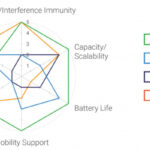
How does HaLow’s battery life compare with other LPWANs?
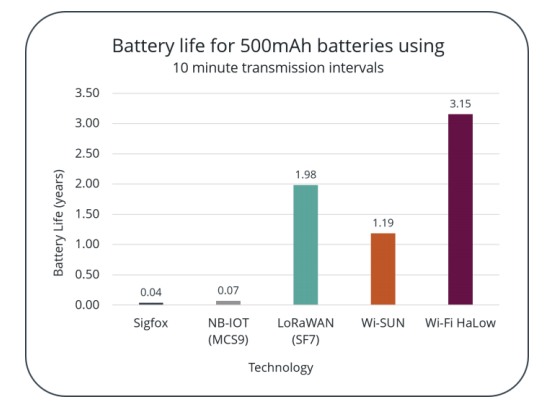
This is a difficult question to answer. According to the Wi-Fi Alliance, all LPWANs provide battery life in years. Most LPWANs state that battery life is from 10-15 years. Wi-SUN has stated battery life of up to 20 years. The results shown in Figure 6 were based on 10-minute transmission intervals using 500mAh batteries.
The battery life varies based on the setup and how the devices are used. Factors such as how frequent data transmissions will occur and data packet size play a role. It is tough to compare unless identical setups are used and measured over the actual life of the batteries. Most of the numbers derived are based on calculations of projected use. It is, therefore, important to evaluate the technology carefully, taking into account all considerations.
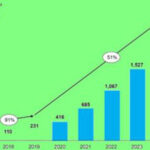
What is the projected growth of HaLow?
According to ABI Research, a global tech market advisory firm, Wi-Fi HaLow is in the early stage of growth, with chipset shipments expected to grow from 4 million in 2021 to 34 million in 2026, at a CAGR of over 50%.
Indeed, most major manufacturers are taking a wait-and-see position at this stage while the startups are taking the lead.
The Wi-Fi Alliance will start the HaLow product certification this Fall.
Who will be the winner(s) of LPWAN?
Most LPWAN technologies can provide practical options for IoT applications such as transportation, asset tracking, smart buildings, telehealth, agriculture, warehouse, and others; it takes more than technologies to succeed in the market.
History of the technology, market reputation, and the ecosystem’s success are all factors that will impact the success of the technology. For example, Z-Wave, Connectivity Standards Alliance (formerly Zigbee Alliance), dominates smart home applications today. Wi-SUN Field Area Networks is the leader in power grids and is expected to expand into smart city applications. Currently, Wi-SUN has a track record in smart cities. City of London and other major cities in Europe are using Wi-SUN. HaLow is a great technology but is still trying to gain momentum in the marketplace.
“Each low-power wide area network has its own advantages and challenges, making each one suitable for different use cases. Wi-Fi HaLow uses license-free bands, is easy to deploy, offers power-efficient data transmission, and runs on a familiar network; however, it is still in the early stages of development, and there are few chipsets available,” according to Stephanie Tomsett, Research Analyst, ABI Research, “it will require large amounts of development and work from the market to ensure that its uptake within the market will increase.”
The real answer is only time will tell.



Leave a Reply