Sometimes when you’re working with a microcontroller unit evaluation board, you need to connect a ribbon cable to the board’s header. If the ribbon cable isn’t specified, how do you know what to order that will fit the header on the MCU board? The pitch of a connector refers to the distance between the pins on a connector. If you don’t have a datasheet or a known part number for a connector, determining the pitch of the connector can be difficult, especially if the distance between the pins (pitch) is very small (often the case).
A pin header, often simply called a header, is an electrical connector with one or more rows of exposed male pins set in a plastic base. A header with female connections is referred to as a header connector. A header or header connector is often a main junction or connection point for interfacing one piece of equipment or device to another. Headers are used to connect with a ribbon cable, or as “jumpers” where electrical connections are made from pin-to-pin or where alligator clips can be temporarily attached.
A jumper can also be called a shunt and is used to quickly connect one pin or terminal to another. Many development boards use a jumper instead of a switch. For example, you might have to set a jumper for boot-up mode and then move the jumper to another position for programming mode. A header with just one pin is a test point. Other names for headers are: board-to-board connectors (for connecting printed circuit boards to each other), terminal strips, pin strip headers (usually a single row of pins set in a plastic base) and board stackers (since they can be used to set a daughter card, for instance, on top of another board). For the newest of newbies, you might want to know that a male connector has pins and a female connector is also called a receptacle and has holes. Putting them together is called mating (I didn’t make this stuff up, folks. But someone has to tell the newbies about the birds and the bees in the electronics world.)
Connector pitch (distance between pins)
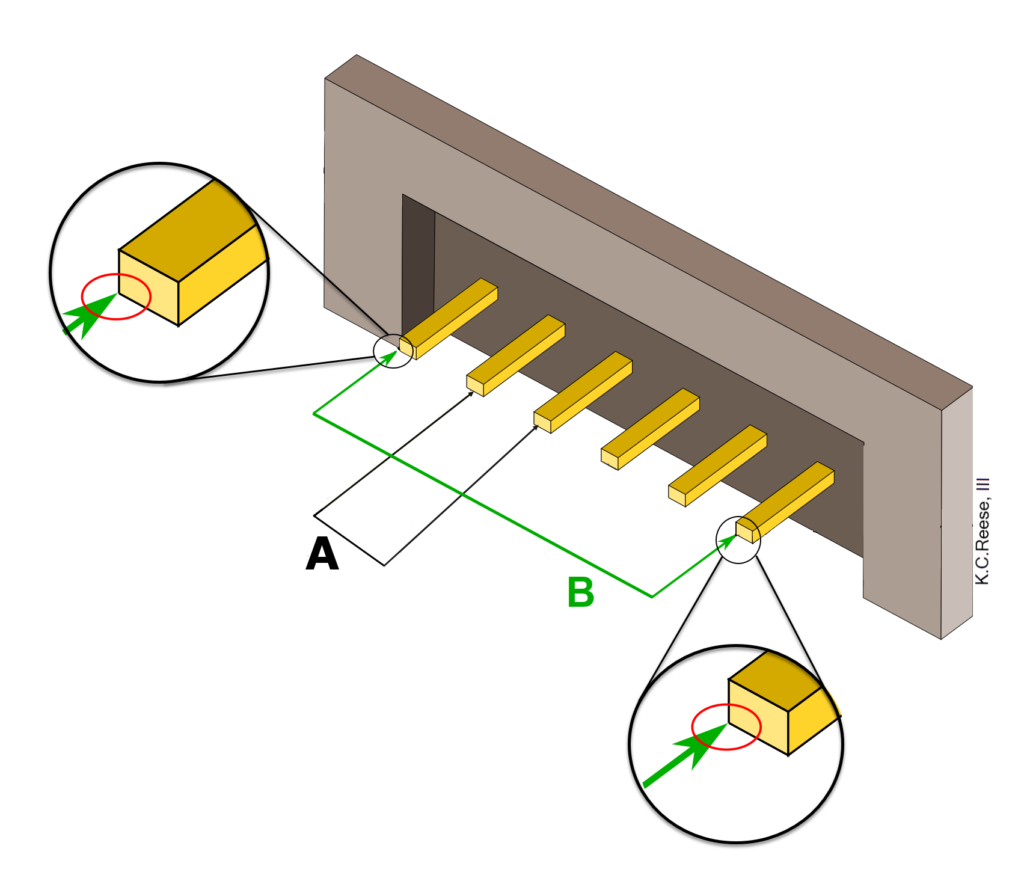
The pitch of a header is measured from the center of one pin to the next (Figure 1, measurement A). If that’s difficult to do with accuracy, you can measure pitch another way. Referring to Figure 1, to measure the pitch (A) of a pin header, measure from the outside edge of the first pin to the inside edge of the last pin (B). Then count the number of pins in the row (C). The pitch, equivalent to A, is equal to B/(C-1), or A = B/(C-1).
If there are two or more rows of pins on the header, then you will want to measure the distance between each row as well. The pitch of the connector is not always the same as the pitch of the ribbon cable, however. A two-row connector with pin spacing at 0.1 inches (2.54 mm) will require a ribbon cable pitch at half of the connector mating pitch, or 0.05 inch (1.27 mm, the most common pitch on ribbon cables).

To measure the pitch of a ribbon cable, measure the cable from outside-edge to outside-edge of the cable, then divide by the number of conductors. Ribbon cable conductors are also called “ways.” This means that a ribbon cable with eight conductors would be called 8-way ribbon cable. Most rainbow-hued ribbon cables are colored in order of resistor values. The red stripe of an all-gray ribbon cable usually means that the red conductor is connected to pin 1.

Is your first image correct? A appears to be demonstrating the distance between a pin and another pin that is 2 pins away, not an adjacent pin. The verbal description seems to contradict the image and its confusing.
Yes, you are right! Fixed!
Cool article but now the diagram shows the measure from the center of one pin to the left edge of the adjacent pin. I think this is meant to be a center-to-center measurement.