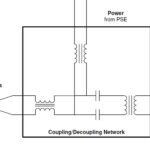
This article begins with a brief review of the operation of CMIs and then looks at how the CDN fits into SPE designs and the specific role of CMIs.
A CMI blocks high-frequency noise common to two power or data lines. It allows direct current (DC) power or lower frequency signals to pass with minimal attenuation. Common mode noise can corrupt and disrupt data transfers. Common noise sources include radiated radio frequency interference (RFI) from unshielded devices like inverters and motors.
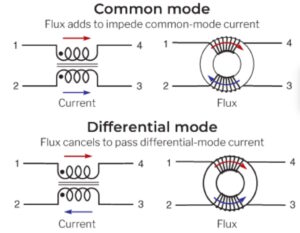
In a CMI, the current in the two lines travels in the same direction, and the combined magnetic flux creates an opposing field that blocks the noise. That contrasts with a differential mode inductor (DMI) where the currents flow in opposite directions, and the flux cancels, so the field does not oppose signal transfer, as shown in Figure 1. Some of the key specifications for CMIs include:
- Impedance rating is related to the amount of noise attenuation required.
- The frequency bandwidth of the anticipated noise determines the frequency range.
- The current rating is determined by the maximum temperature rise allowable for the inductor.
SPE CDNs
The CDN’s CMI is designed to balance the signal, making it symmetrical and ensuring no common mode noise interferes with the differential mode information. A CMI with a large common mode impedance and small differential mode impedance is required to filter the common mode noise without damaging the integrity of the information carried on the differential signal,
Mode conversion is another consideration when selecting CMIs. The more turns on an inductor with a given winding technology, the higher the mode conversion between differential and common mode. High mode conversion is bad for signal integrity since more of the differential signal is converted into the common mode in some frequency ranges. Return loss, the ratio of the reflected signal to the incident signal, must be minimized in the CMI for best system performance.
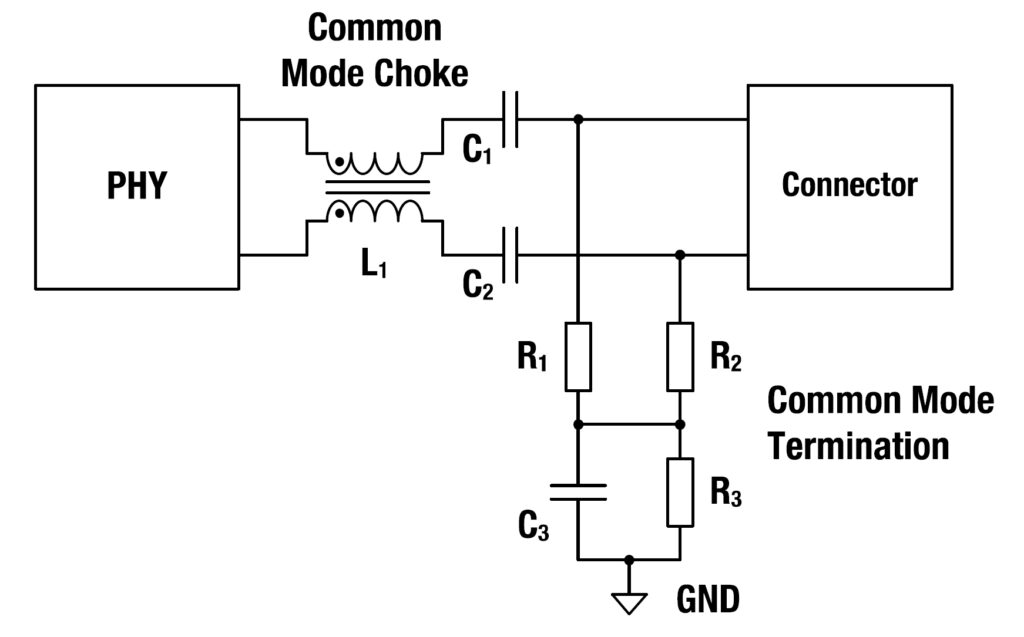
The CMI is a key component in the common mode termination, matching the network to the ground at the connection point between the network cable and the SPE electronics, as shown in Figure 2. The network consists of three resistors and one capacitor. R1 and R2 are typically 1 kΩ and terminate the wires balanced to ground, minimizing interfering common mode signals. Decoupling of direct currents is ensured by C3, a 1000 nF capacitor, and R3, a 100 kΩ discharge resistor. In addition to the termination network, two small capacitors, C1 and C2, typically 100 nF and 50 V, are used with cable lengths of up to 15 meters, as are common in low-voltage designs found in automotive SPE applications.
Summary
The CMI connects the SPE electronics to the network cabling and protects the data lines from high-frequency noise. Key specifications include impedance, frequency range, and current rating. Mode conversion and return loss are also important performance considerations. The CMI is part of the common mode termination network, which supports robust connectivity.
References
A Guide to Understanding Common Mode Chokes, Coilcraft
Single Pair Ethernet for Industrial Applications, SPE Industrial Partner Network
Single Pair Ethernet: How to implement 10Base-T1L, TDK