Single-Pair Ethernet (SPE) is defined in IEEE 802.3 and adapts the basic Ethernet standard to use a single wire pair. Power over data line (PoDL) is sometimes referred to as power over Ethernet (PoE) adapted for SPE. That’s only partially correct; PoDL is optimized specifically for automotive and similar environments, and the newer single pair power over Ethernet (SPoE) standard was developed for SPE in the industrial Internet of things (IIoT) and Industry 4.0.
SPE is defined for operation on a single balanced pair for automotive applications in IEEE standards like:
- 3cg (10BASE-T1) with bandwidth from 0.1 to 20 MHz and reach up to 1000 m.
- 3bw (100BASE-T1) with bandwidth 0.3 to 66 MHz and reach up to 40 m.
- 3bp (1000BASE-T1) with bandwidth 1 to 600 MHz and reach up to 40 m
- 3ch for 2.5 Gb/s, 5 Gb/s, and 10 Gb/s for distances up to 10 m
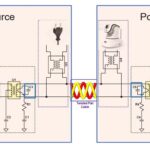
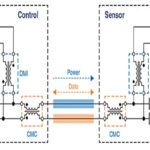
New standards to support operations up to 25 Mb/s are under development. SPE is being adopted well beyond its automotive roots. As noted above, SPoE was developed for IIoT and similar applications. In addition, the Aeronautical Radio, Incorporated (ARINC) 854 Cabin Equipment Network Bus standard details the use of SPE for 15 meters or less in commercial aircraft. While traditional Ethernet uses two pairs (10/100M) or four pairs (1G and above), SPE uses a single pair of wires for high-speed data transmission (Figure 1).
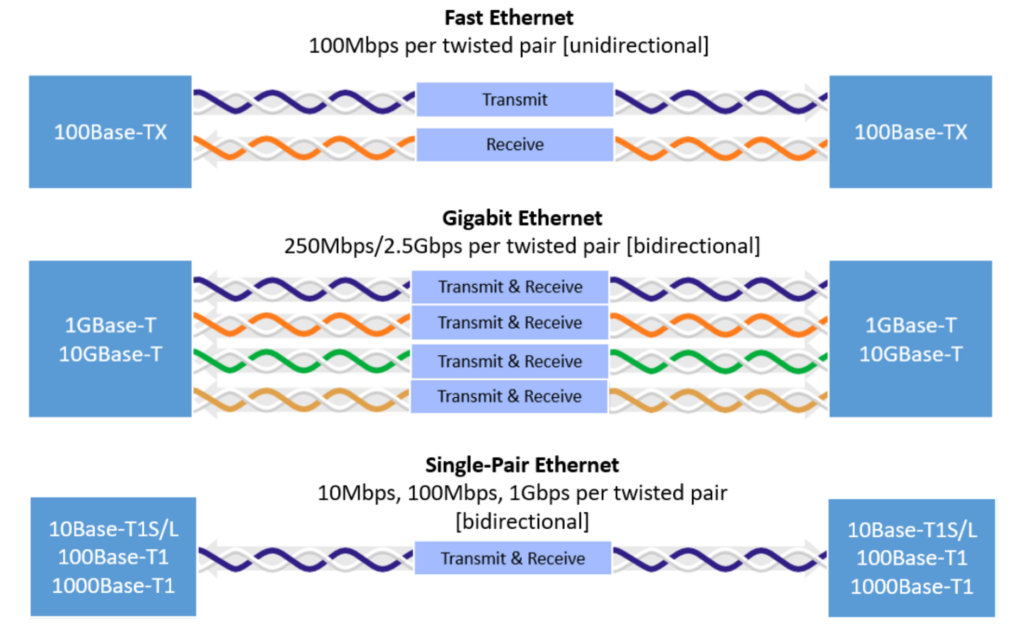
Cables and connectors
There are several standardized SPE cable types based on data rates and installation flexibility, including:
- For 10 Mbit/s networks with up to 1000 m cable length
- IEC 61156-13 – SPE data cable with 20 MHz bandwidth for fixed installation
- IEC 61156-14 – SPE data cable with 20 MHz bandwidth for flexible installation
- For 1 Gbit/s networks up to 40 m cable length
- IEC 61156-11 – SPE data cable with 600 MHz bandwidth for fixed installation
- IEC 61156-12 – SPE data cable with 600 MHz bandwidth for flexible installation
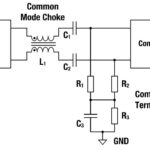
New types of connectors were needed for SPE and are defined in the IEC 63171-6 standard. The standard includes various connector styles, M8 and M12 types, and various ingress protection (IP) ratings (Figure 2).

SPE Power
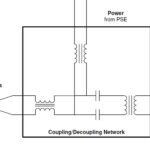
SPoE is an extension of the original PoDL standard. PoDL was designed for use in automotive networks and other embedded systems. The original PoDL power classes defined various power levels from 0.566 to 65.3 W for regulated and unregulated voltages of 12, 24, and 48 Vdc. Clause 104 of IEEE 802.3 was expanded for 10BASE-T1S/T1L by adding SPoE power classes 10 to 15 for use in industrial networks and building automation systems.
The power classes in SPoE are defined for operational technology (OT) networks like the IIoT. Power delivery using 20, 24, or 30 Vdc is defined in classes 10, 11, and 12, for long, medium, and short cables, respectively. Power delivery using 50, 55, and 58 Vdc is defined in classes 13, 14, and 15 for long, medium, and short cables, respectively. Unlike PoDL, SPoE does not categorize the classes as regulated or unregulated. Depending on the voltage and cable length, SPoE can deliver from 1.23 W to 52 W.
Summary
SPE is a comprehensive set of standards. Initially developed for automotive environments, it’s being expanded for the IIoT, industrial and building automation, and commercial aircraft applications. Like the original Ethernet standard, SPE includes a separate annex defining the simultaneous power and data delivery over a single cable.
References
OPEN Alliance
PoE and PoDL Standards Explained, AEM Test
Single Pair Ethernet, SPE Industrial Partner Network
What Are The Benefits of Single-Pair Ethernet?, Remee Wire and Cable
What is Single Pair Ethernet?, BotBlox