Analysis and possible pushback from users may be among the next steps in the development of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). NIST has started the process of standardizing the four finalist algorithms. That’s the last step before developing the mathematical tools and making the tools available so developers can integrate them into the global encryption infrastructure.
This FAQ looks at how organizations, including the National Security Agency (NSA), Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), Verisign domain name registry services, and cloud computing organizations, are reacting to and preparing for the deployment of PQC.
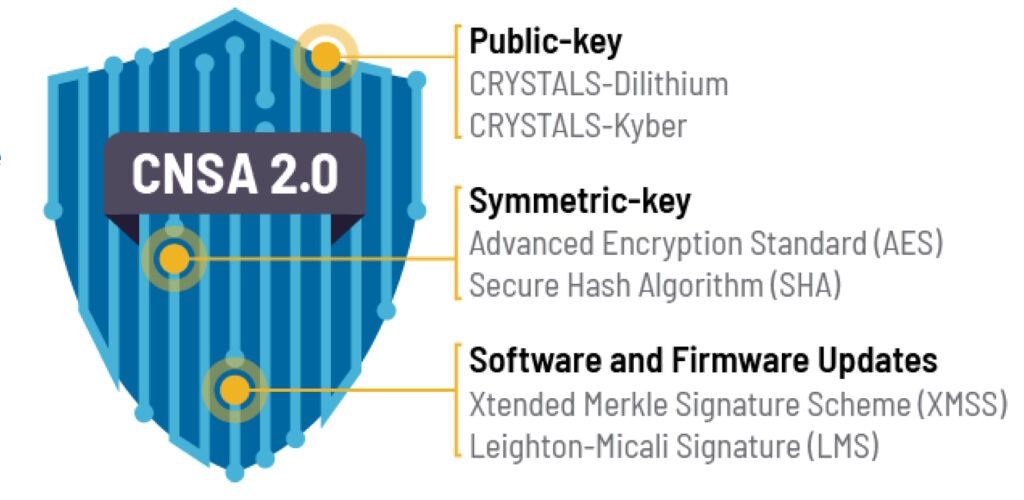
PQC algorithms are expected to be secure from cryptanalytic attacks by quantum computers. The NSA recently announced the Commercial National Security Algorithm Suite 2.0 (CNSA 2.0). It includes three elements, public keys, symmetric keys, and software and firmware updates (Figure 1). The signature use cases are the most critical, and the NSA is encouraging its vendors to begin adopting NIST signatures immediately. It’s anticipated to be a long process, and the NSA expects the transition to PQC algorithms for national security systems to be complete by 2033.
PQC and critical infrastructure
CISA has its own PQC initiative to address the threats that will result from the deployment of quantum computing and has identified the transition to post-quantum encryption as a priority. CISA requires that government and critical infrastructure organizations make coordinated preparations to implement the NIST PQC standards scheduled for publication in 2024.
CISA, together with the Department of Homeland Security, has developed a Post-Quantum Cryptography Roadmap. The first step in preparation is the identification and inventory of vulnerable critical infrastructure systems across the 55 National Critical Functions (NCFs). NCFs are defined as functions of government and private industry so vital that their disruption, corruption, or dysfunction would have a debilitating effect on security, the economy, and/or public health or safety. Each individual NCF has already been analyzed, and specific security risks from quantum computing have been identified.
Verisign’s DNSSEC
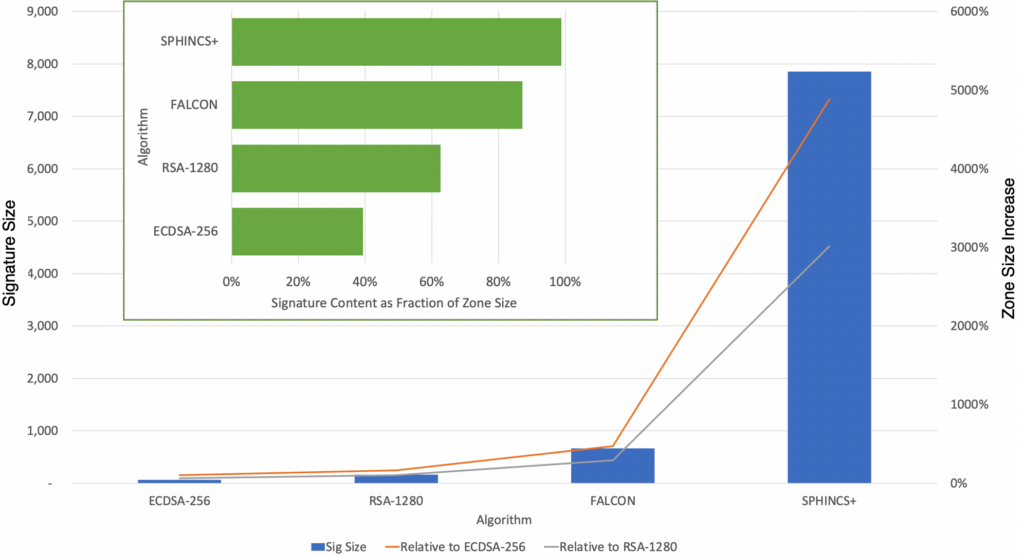
Verisign has begun analyzing how to apply the NIST PQC algorithms to Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC). Verisign has indicated two potential concerns related to the size of the NIST PQC algorithms (Figure 2):
- The NIST PQC algorithms have signature sizes that are up to two orders of magnitude larger than existing signatures and would result in DNSSEC responses that exceed the size limitations of existing systems. The Transmission Control Protocol and other mechanisms could handle the larger signatures but require additional overhead that would slow responses and are undesirable for use with every signature.
- The large signatures require significantly more memory capacity. That creates challenges for resolvers using in-memory caches and authoritative nameservers using in-memory databases.
PQC in the cloud
Cloud security posture management (CSPM) is an automated set of security protocols. CSPM is designed to identify and correct cloud misconfiguration and for compliance monitoring to identify potential security gaps. CSPM tools examine cloud environments and compare them to best practices and known security risks. That can also involve enforcing encryption levels of information at rest or in transit, including encryption keys and event logging and tracing. Various suppliers of CSPM software and services are analyzing the impact of the NIST PQC algorithms to determine how or if they can be integrated into existing compliance monitoring solutions.
Summary
Now that NIST has identified the first group of PQC algorithms, a range of government and industry organizations are analyzing them to determine their impact on existing security protocols and processes. In most cases, analysis and potential integration of PQC algorithms is a high-priority activity.
References
Improve Post-Quantum Cryptography Security with CSPM, Trend Micro
Next Steps in Preparing for Post-Quantum DNSSEC – Verisign
Post-Quantum Cybersecurity Resources, National Security Agency/Central Security Service
Post-Quantum Cryptography Initiative, Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency