 Intrinsic ID announced Zign RNG, a new offering enabling IoT chip providers and device makers to establish a high-security random number generator in software enabling it to be deployed on devices even after silicon fabrication to ensure a true source of randomness for IoT devices.
Intrinsic ID announced Zign RNG, a new offering enabling IoT chip providers and device makers to establish a high-security random number generator in software enabling it to be deployed on devices even after silicon fabrication to ensure a true source of randomness for IoT devices.
Random number generators (RNGs) are essential for cryptographic applications and form the foundation of security systems. For IoT devices, an RNG is generally implemented by incorporating hardware peripheral controllers, which are proving to be imperfect as a source for real randomness because they start with a deterministic input. A report from Bishop Fox shows critical vulnerabilities have been disclosed in hardware random number generators used in billions of Internet of Things (IoT) devices whereby it fails to properly generate random numbers, thus undermining their security and putting them at risk of attacks.
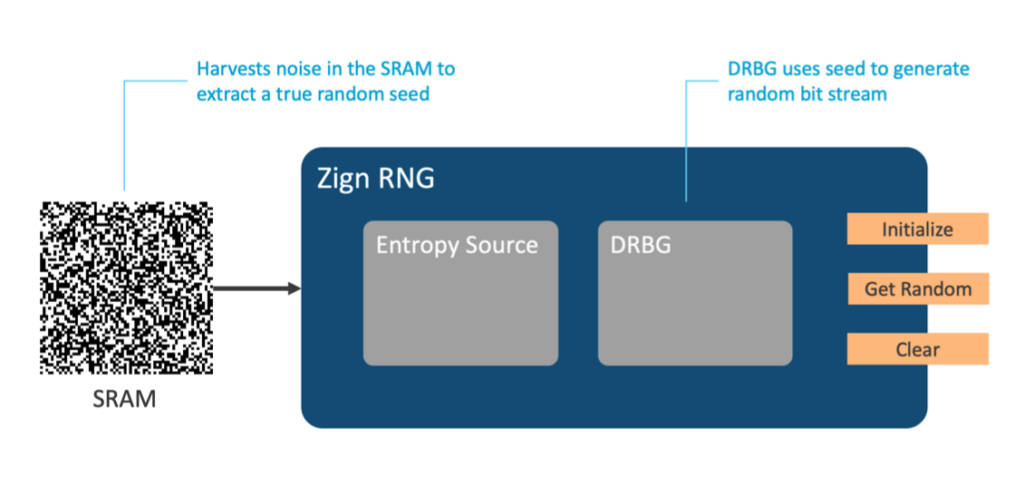
The Intrinsic ID Zign RNG extracts a true random seed harvested from noise in the SRAM PUF enabling IoT device makers to ensure confidentiality, authentication, and communication integrity. This makes Zign RNG the first and only embedded software implementation with a hardware entropy source option that does not have to be loaded at silicon fabrication. Zign RNG can be installed later in the supply chain, and even retrofitted on already-deployed devices. This provides a never-before-possible “brownfield” deployment of a cryptographically secure NIST-certified RNG.
The Zign RNG product is compliant with the NIST SP 800-90 standard. It implements a deterministic random bit generator (DRBG) as specified in NIST SP 800-90A. This means that a strong RNG solution in software is created on top of an existing SRAM memory.
Zign RNG has passed all standard national institute of standards and technology (NIST) randomness tests and is a NIST/FIPS-compliant software solution that addresses the issue of Hardware RNG peripherals used in IoT devices running out of entropy and leaving the device vulnerable.
Zign RNG is available immediately and is ideally suited for anyone making devices or chips for IoT. Zign RNG can be implemented at any stage of a device’s lifecycle, even after a device is already created and/or deployed in the field.


Leave a Reply