JESD209-6, the recently released LPDDR6 (low power double data rate 6) standard by JEDEC, represents a significant leap forward in memory technology, particularly for devices with limited power budgets. It’s crucial for the next generation of mobile devices, AI applications, and edge computing, where high performance and power efficiency are paramount. It’s also expected to help limit power consumption in data center applications.
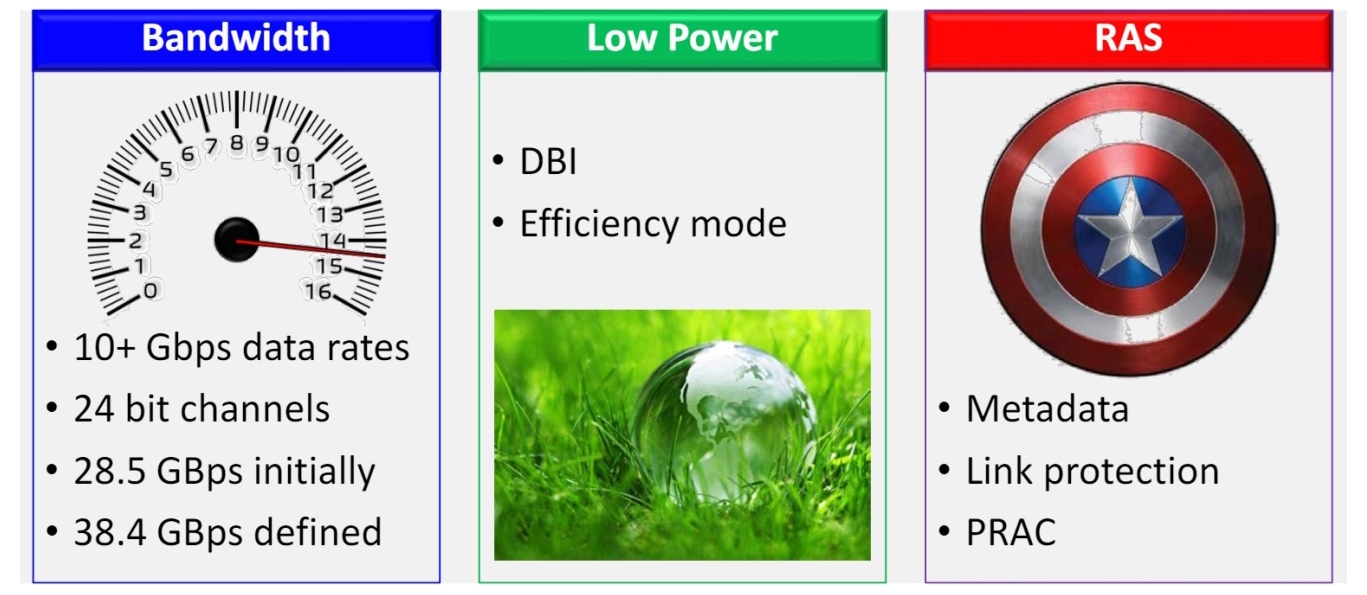
Some key features and improvements include increased bandwidth, with a path up to 38.4 Gbps, lower energy consumption, and enhanced reliability, availability, and serviceability (RAS).
For example, data bus inversion (DBI) is designed to enhance both performance and power efficiency in memory operations. Per row activation counting (PRAC) helps maintain DRAM data integrity by monitoring and managing row activations, safeguarding against potential data corruption. (Figure 1).
Delving into details
A combination of architectural and design improvements enables LPDDR6 to deliver a maximum bandwidth up to 38.4 GB/s on a 64-bit bus, double the initial capability of LPDDR5. LPDDR6 also provides greater flexibility, enabling finer tuning and performance optimization.
The dual sub-channel architecture supports 12 data signal lines (DQs) and four dedicated command/address (CA) signals per sub-channel, enabling both faster data access and the ability to optimize channel performance as demands vary.
Channel widths in LPDDR6 have been increased to 24 bits compared with 16 bits in LPDDR5. Combined with dual sub-channels, the wider channel provides further enhancement to overall memory bandwidth. That can result in a bandwidth increase from 64 to 96 bits in smartphones and from 128 to 192 bits in laptops.
Finally, LPDDR6 supports real-time burst length control between 32- and 64-byte bursts, helping optimize both bandwidth and power consumption. That can be particularly important in edge devices handling variable AI workloads.
There are several new tools for reducing power consumption, including DBI and the addition of a second power domain. DBI supports power and noise reduction.
If a predetermined threshold of ‘0’ bits is reached, the entire byte is inverted with all bits flipped from 0 to 1 and vice versa. A dedicated DBI bit is used to indicate that the data has been inverted. Inversion is designed to reduce the number of high-to-low transitions, reducing switching noise and power consumption.
LPDDR6 also supports more sophisticated power management with two efficiency modes. Static efficiency mode is designed for sustained high-throughput AI workloads. Dynamic efficiency mode helps optimize the performance of low-bandwidth scenarios like processing sensor data.
A single sub-channel is used when operating in dynamic efficiency mode. In addition, LPDDR6 has added a second voltage domain, VDD2, that supports dynamic voltage and frequency scaling for low power (DVFSL) during periods of low activity.
Reliability
Of course, high bandwidth and low power consumption aren’t useful if the data is not reliable. LPDDR6 has several features dedicated to ensuring RAS. PRAC monitors and manages row activation, helping ensure data integrity. Memory built-in self-test (MBIST) supports in-situ testing, aiding in diagnostics and troubleshooting of potential issues.
LPDDR6 supports on-die error correction code (ECC) for detecting and correcting memory errors at the hardware level and command/address (CA) parity for detecting errors during command and address transmissions.
If errors are detected, the error scrubbing function helps correct errors in memory cells as they occur, before they can accumulate and impact system reliability. Carve-out meta mode supports allocation of specific memory regions for crucial tasks, isolating and protecting vital data and operations.
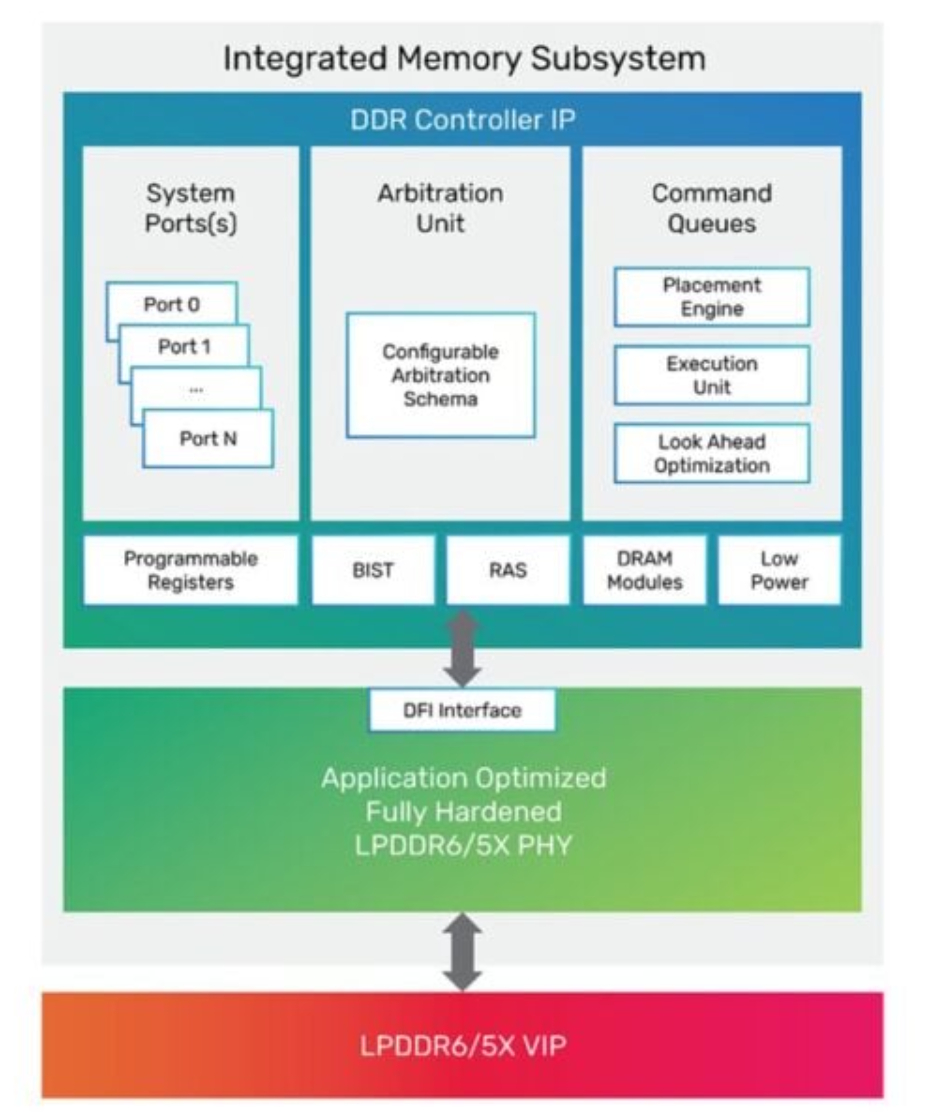
LPDDR6 memory controllers
LPDDR6 memory controllers are already available. Some support both LPDDR6 and LPDDR5 to enable a smooth transition between the two generations of technology. Controllers are available that support native integration into monolithic systems on chip (SoCs) and multi-die solutions.
Support for advanced memory interfaces like the Arm AMBA AXI bus are available. Memory controllers are offered as a reusable block in the form of a soft register transfer level (RTL) macro (Figure 2).
Summary
JESD209-6, commonly called LPDDR6, has been optimized for running AI applications on power-limited platforms like smartphones and laptops. Compared with LPDDR5, it offers increased bandwidth, lower energy consumption, and enhanced reliability, availability, and serviceability. Initial LPDDR6 controller IPs are available that also support LPDDR5 to simplify the migration to the new technology.
References
Cadence Introduces Industry-First LPDDR6/5X 14.4Gbps Memory IP to Power Next-Generation AI Infrastructure, Cadence
Comprehensive LPDDR6 Solution for End-to-End Memory Design and Test Workflows, Keysight
JEDEC LPDDR6 Specification: Key Features and Benefits, guru3d
JEDEC Releases New LPDDR6 Standard to Enhance Mobile and AI Memory Performance, JEDEC
JEDEC Reveals Massive Speed Boosts For Next-Gen DDR6 And LPDDR6 Memory, Hot Hardware
LPDDR6 Is Coming: Are You Ready?, Introspect Technology
LPDDR6 likely to debut in 2026 as JEDEC publishes new standard document and targets mobile devices and AI – desktop PCs and workstations will have to wait, Tech Radar
Next-gen DDR6 memory teased: DDR6-8800 up to a possibly insane DDR6-21000 memory, Tweak Town
EE World related content
What is the HPC memory wall and how can you climb over it?
How can silent data corruption be detected and corrected in AI systems?
What interconnects are used with memory for HPC and AI?
How does the Zenoh protocol enhance edge device operation?
What’s the difference between GPUs and TPUs for AI processing?



Leave a Reply