If the Internet of Things (IoT) is about connecting objects like a thermostat or a pacemaker to the Internet Protocol (IP)-based networks, then it’s even more about securing links to these objects. And that includes implementing security while connecting IoT devices to a cloud platform.
The good news is that securing links to the cloud is no more a drain for IoT developers. Traditionally, embedded designers required significant time and resources for creating cloud-connected applications. It included the necessary expertise in communication protocols, security, and hardware compatibility. That’s no more the case.
Again, like simplifying the communication links between IoT nodes and cloud, MCU suppliers are joining hands with cloud service providers to ensure that designing secure cloud-connected systems is no more an exhaustive process.
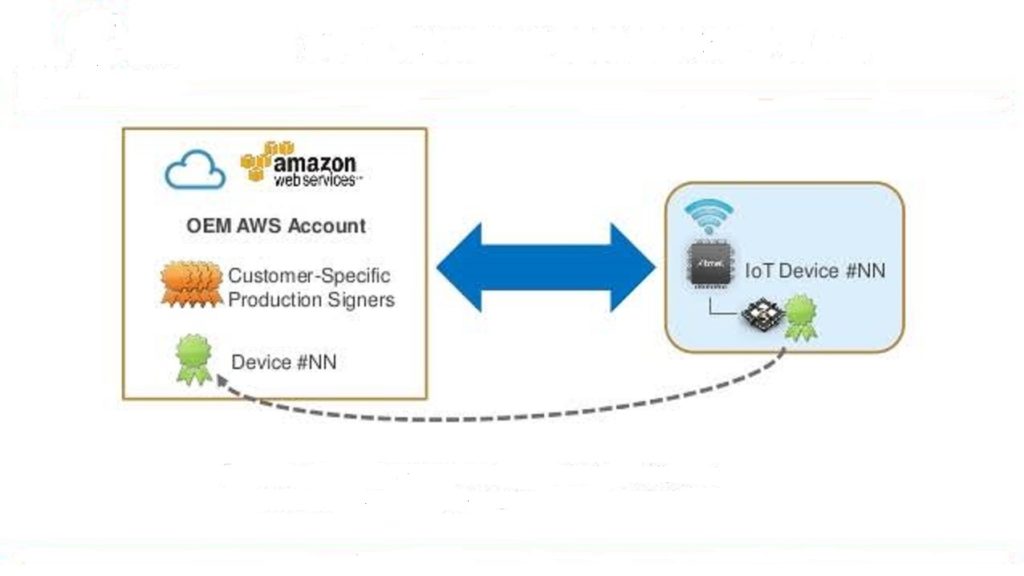
Here, it’s worth mentioning that the MCU-based hardware solutions can store unique device credentials, and they can connect IoT devices to the cloud much faster than software-only alternatives. Also, the software can be copied, reverse-engineered, and exploited with ease. On the other hand, the hardware-based solutions allow the identity of an IoT device to be programmed into the microcontroller chip at a secure factory location.
About TLS and wolfSSL
The communication links to the cloud often rely on protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Socket Layer (SSL) to protect the confidentiality of messages. The TLS protocol and its predecessor, SSL protocol, are widely used to securely transfer the data between the client (IoT node) and the server (cloud computer) through authentication, encryption, and integrity mechanisms.
TLS, an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard for secure communication, is employed to secure HTTP communications over TCP-based links. Datagram Layer Transport Security (DLTS) performs similar functionality for the UDP links.
Though commonly known for encrypting data transport in accessing websites and other web applications, the security protocol’s TLS 1.2 version is becoming the de facto standard for connecting embedded systems to a network. That’s why cloud services such as AWS IoT require that the IoT device must authenticate itself during the TLS handshake using a device-specific authentication mechanism.
The IoT developers also commonly employ wolfSSL, a lightweight C-language-based SSL/TLS library, which is targeted at embedded, RTOS, and resource-constrained environments primarily because of its small size, speed, and portability features.
Hardware-based security
The TLS and SSL add encryption support to connections linking IoT devices to the cloud. However, while TLS 1.2 is undeniably robust, an embedded system still requires a unique, secure, and trusted identity to prevent remote attacks.
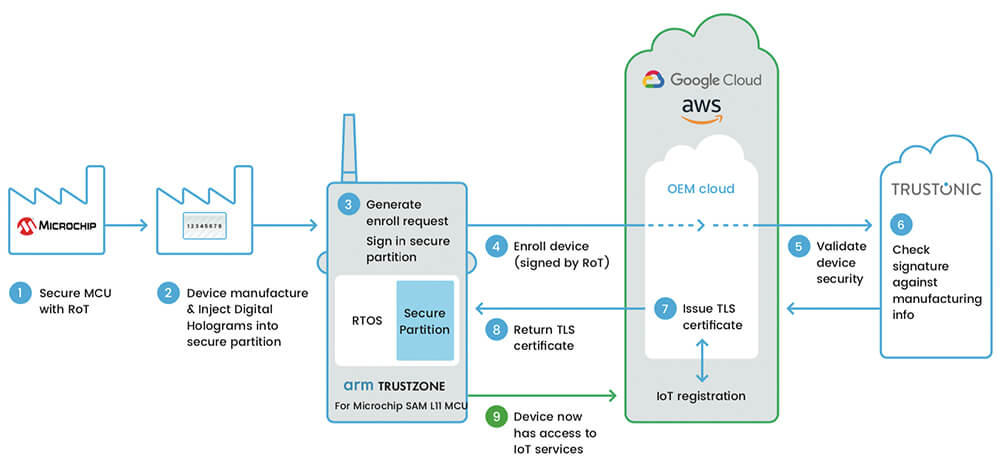
That’s where microcontrollers enter the IoT equation by providing a built-in hardware security engine to harden the TLS-based communications. They enable IoT devices to be hardened with strong cryptography and thus prevent malicious attacks from hackers and cybercriminals.
As compared to other security chips, MCUs offer design simplicity for securing cloud links due to fewer avenues of attack. The fact that code on MCUs runs “bare metal” and that MCUs include no intermediary operating system (OS) to execute instructions means that they have a limited number of potential attack vectors.



Leave a Reply