Zero-touch provisioning eliminates the manual labor needed to connect devices to a network and allows these devices to be provisioned and configured automatically. It’s especially critical for small and mid-size companies in terms of cost and time of managing the provisioning logistics.
While it’s a common concept in the networking industry at large, MCU suppliers like Microchip are introducing it to simplify the secure connections between IoT devices and cloud services like AWS. It’s a fully managed service aimed at further simplifying the development process for securing the IoT connectivity.
In a secure connection between an IoT edge device and a cloud platform, zero-touch provisioning automatically completes the registration to the cloud platform after establishing the device identity. That’s how it can save embedded engineers a lot of development time and expensive security engineering expertise. Moreover, it can save the cost of third-party provision services and certificate authorities.
A design case study
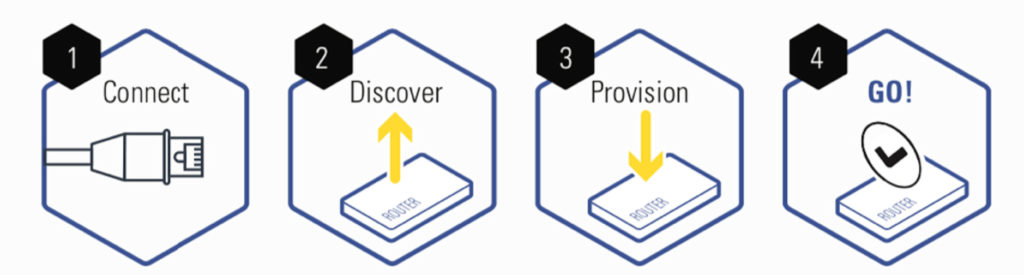
The idea of zero-touch provisioning may sound simplistic, as its name suggests, but it’s still important to know how it works. Take the example of Microchip’s AWS Zero Touch Secure Provisioning Platform that securely connects IoT devices to the Amazon Web Services IoT (AWS IoT) platform in three steps.
First, a design kit, AT88CKECCAWS-XSTK, enables developers to meet the AWS’s mutual authentication model requirements while connecting to the AWS IoT cloud during the evaluation and engineering phase. Here, it’s important to note that the kit leaves the handling of certificates and keys to MCU supplier’s secure provisioning facilities; in this case, secure provisioning is carried out at Microchip’s factories during the production stage.
Second, the security-centric MCUs like ATECC608A, which are pre-configured for the AWS IoT framework, assist developers in complying with security standards during the prototyping and pre-production phase. In the third and final phase, IoT devices are customized for the production stage.

Now, designers can simply solder the security MCU or crypto element on the board and connect it over I2C to the host MCU, which already runs an AWS SDK to leverage the security MCU features. Microchip and AWS have jointly developed this zero-touch provisioning platform to allow developers to carry out mutual authentication with a remote server authorized on the AWS cloud.
A shield against human errors
In short, install the IoT device and switch it on; it will automatically register itself to the cloud platform like AWS IoT. Next, the cloud platform will start sending the required configuration, application files, etc.
The zero-touch provisioning kits come with an easier on-boarding process that generates certificates or keys and provisions them into security devices like MCUs. That, in turn, reduces operations and interactions with cloud platforms.
Besides the security labyrinth, zero-touch provisioning enables developers to bypass the complications associated with communication protocols and hardware compatibility issues. Last, but not least, it acts as a shield against human errors and software loopholes.



Leave a Reply