Factories have always set their sights on increased productivity and cost reduction and the Industrial Internet-of-Things (IIoT) has impacted modern factories in a big way. To achieve those goals, modern factories have made automation and preventive maintenance using robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and edge computing top priorities. In the next 10 years, factories with IIoT know-how will excel, while any sticking with older methods are likely to be left behind. This article explores the role of sensors in modern factories and surveys IIoT trends affecting sensors.
At this year’s Sensors Expo, TE demonstrated how preventive maintenance was implemented and retrofitted in an HVAC system that formed part of a smart factory system. In the system, liquid flow and leakage are monitored 24/7 automatically and remotely.
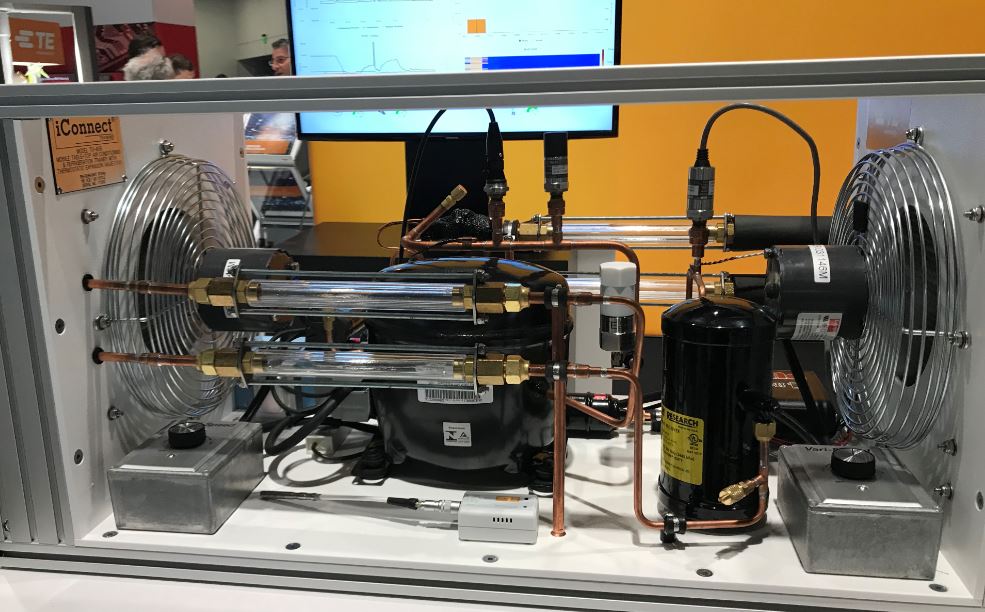

Figure 2 outlines how sensors that are part of the IIoT help create a smart factory. While traditional factories have used automatic equipment for a long time, smart factories go further, integrating more robotics and AI. For example, smart factories can implement 24/7 remote monitoring of automation equipment (item 1) using smart sensors (item 2). The data collected is transmitted wirelessly via LoRaWAN, Bluetooth, cell signals, or Wi-Fi (item 3) to a remote control center (item 4). Note that the control center can be a handheld device with an app. To maximize production, factories may run three eight-hour shifts a day except during scheduled maintenance.
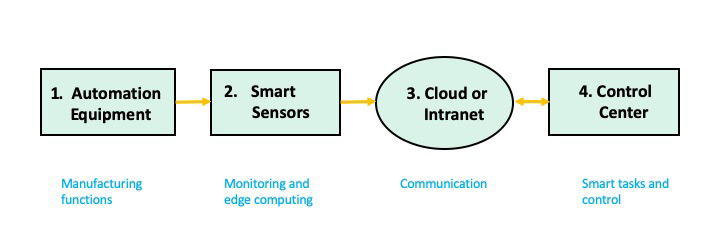
In a scenario where automation equipment, robotics, and many machine tools are on such a schedule, early warnings to prevent equipment breakdown when equipment exhibits abnormal behavior are crucial. Some of the common parameters to be monitored include:
- Temperature
- Vibration and shock
- Electrical current
- Motion
- Position/ proximity
- Pressure
- Fluid/flow
- Force
- Vision
- Gases
What’s next for IIoT sensors?
Future smart factory sensors will have higher precision, integrate multiple sensors in a smaller device, and combine sensing and wireless communication technology. Sensor packaging will be more compact, while the sensors themselves consume less power and lower overall costs. Here are a few examples of what to expect.
Integrating sensor and wireless communication in one package
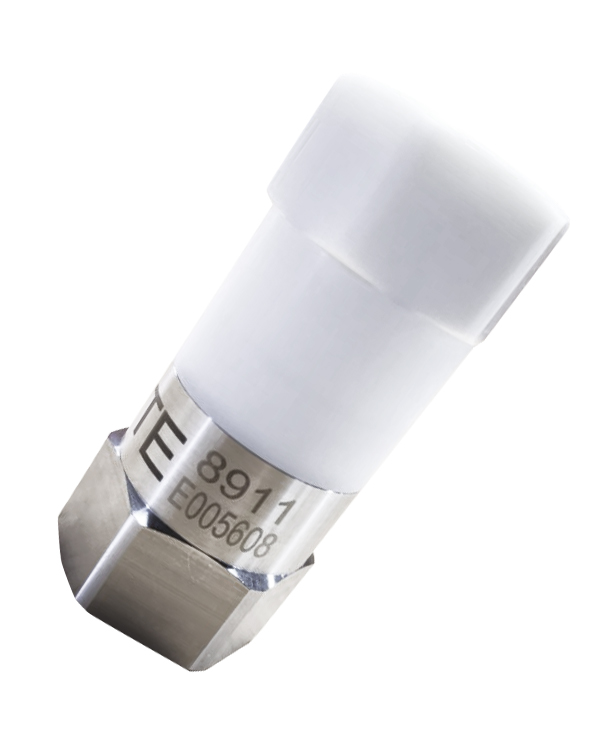
TE’s wireless vibration transmission sensor, now in development, integrates in a single package a battery-operated LoRaWAN radio and a sensor which measures vibration in machines or automation equipment containing motors or pumps. There is no need to wire the sensors to a controller. In addition, the low-power, 868/915 MHz, LoRaWAN wireless technology provides an operating life of five years, important for lowering labor and maintenance costs. A trendsetter, indeed.
Figure 3: TE’s wireless vibration transmission sensor, now in development, integrates in a single package a battery-operated LoRaWAN radio and a sensor to measure vibration. (Source TE Connectivity)
Compact data analysis system
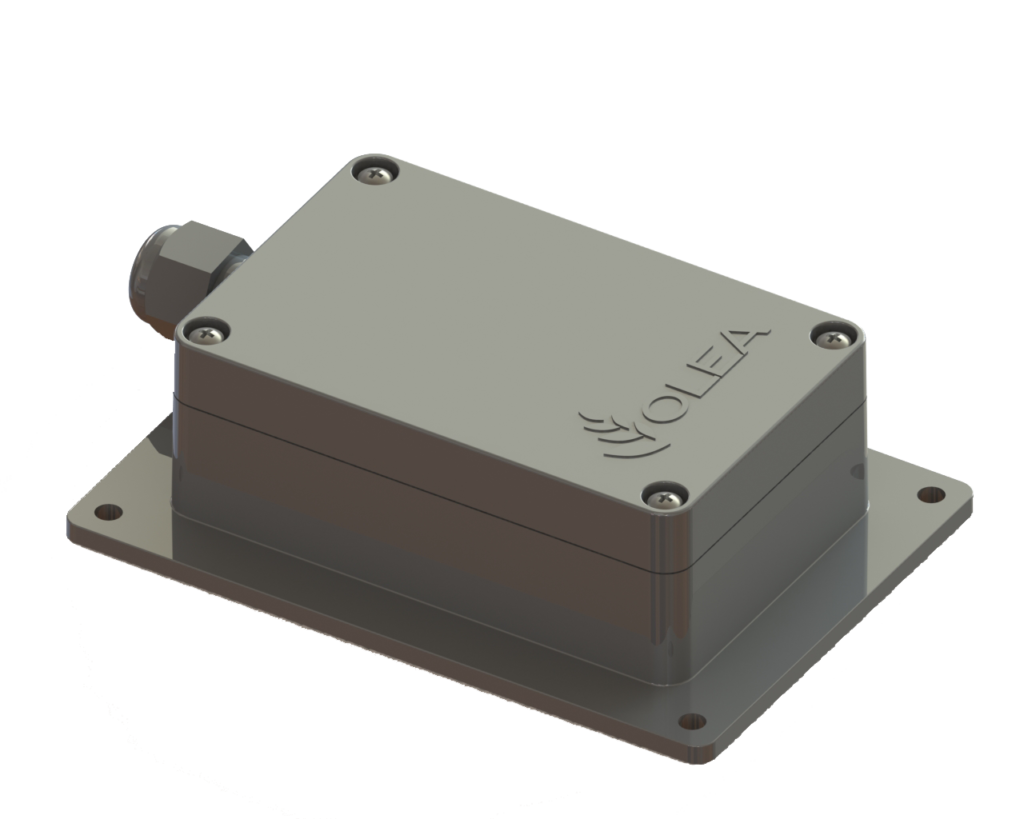
The OleaWave intelligent vibration sensor platform from Olea Sensors Network is a system in a box. Weighing one ounce and measuring 84mm x 35mm x 8.7mm (WxHxD), it includes a 24GHz radar sensor, nine axis motion sensors, and a 32-bit Arm Cortex-based 16-bit data acquisition. Able to measure temperature and vibration, the unit is also to the machine requiring analysis. Data can be extracted via USB 3.0, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi. A Li-Ion battery allows 40 hours of use per recharge. Supported software includes Windows 10, Linux, Android, and iOS.


Leave a Reply