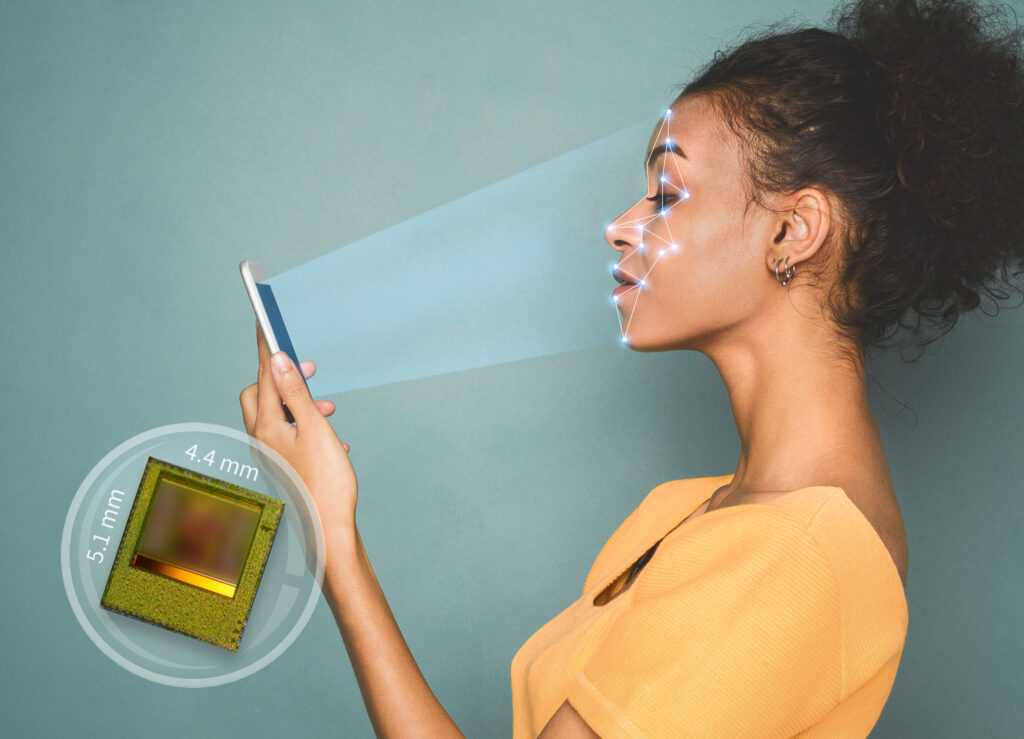
 Reliable face authentication, improved photo functions, and authentic augmented reality experiences: 3D depth sensors assume a key role in smartphones and for applications that rely on accurate 3D image data. Infineon Technologies AG has collaborated with software and 3D Time of Flight system specialist pmdtechnologies ag to develop the world’s smallest and most powerful 3D image sensor.
Reliable face authentication, improved photo functions, and authentic augmented reality experiences: 3D depth sensors assume a key role in smartphones and for applications that rely on accurate 3D image data. Infineon Technologies AG has collaborated with software and 3D Time of Flight system specialist pmdtechnologies ag to develop the world’s smallest and most powerful 3D image sensor.
The new REAL3 single-chip solution measuring just 4.4 x 5.1 mm, is the fifth generation of successful time-of-flight deep sensors from Infineon. Its small dimensions allow it to be incorporated into the smallest devices with just a few elements. The chip also provides the highest resolution data with low power consumption.
The new REAL3 chip meets a range of applications in the areas of security, image use and context-based interaction with the devices. The 3D sensor also allows the device to be controlled via gestures, so that human-machine interaction is context-based and without touch.
The depth sensor time-of-flight technology enables an accurate 3D image of faces, hand details or objects which is relevant when it must be ensured that the image matches the original. When applied in payment transactions using mobile phones or devices that need no bank details, bank cards or cashiers, the payment is carried out via facial recognition. This requires an extremely reliable and secure image and return transmission of the high-resolution 3D image data. The same applies to securely unlocking devices with a 3D image. The Infineon 3D image sensor also implements this in particular in extreme lighting conditions such as strong sunlight or in the dark.
Furthermore, the chip provides additional options for ambitious photos with cameras, for example, with enhanced autofocus, bokeh effect for photo and video, and improved resolution in poor lighting conditions. Real-time full-3D mapping also allows authentic augmented reality experiences to be presented.
Series production will begin in the middle of 2020. In addition, Infineon Technologies offers an optimized illumination driver (IRS9100C) that further improves performance, size and cost as a complete solution. More information on Infineon’s 3D image sensor family can be found at www.infineon.com/real3.


Leave a Reply