Memory management is important in all digital electronic devices, including devices designed for use on the Internet of Things (IoT). It supports efficient resource allocation and memory utilization and prevents memory fragmentation, improving efficiency. It also supports memory protection and device security.
This FAQ briefly reviews the common weakness enumeration (CWE) scheme for identifying software weaknesses like poor memory management, some of the more common memory security problems, and how Capability Hardware Enhanced RISC Instructions (CHERI) can be used to address memory management challenges in C and C++ software.
C and C++ are among IoT devices’ most common coding languages. They are great for creating efficient code but require that developers be well-versed in memory management to properly maintain the stack for storing working variables and the heap for storing longer-lived objects and data structures, or risk creating potential security vulnerabilities.
MITRE Corp. maintains CWE, a community-developed list of common software and hardware weakness types with security implications. CWE defines a “weakness” as a condition that has the potential to contribute to the introduction of one or more vulnerabilities. The goal of CWE is to provide developers with the insights and information needed to eliminate coding mistakes. An important part of implementing CWE is the scoring system.
Common weakness scoring system
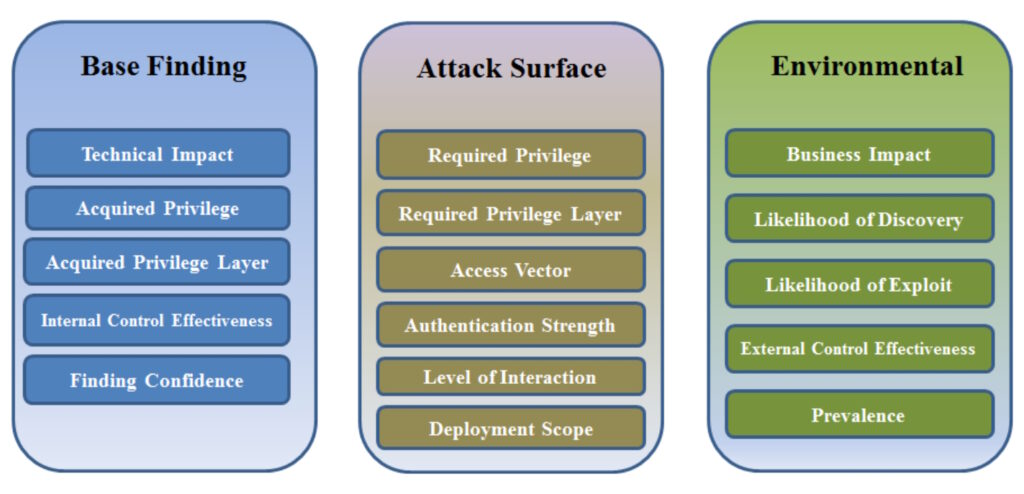
The Common Weakness Scoring System (CWSS) is used to prioritize software weaknesses consistently, flexibly, and openly. It’s organized into three metric groups: Base Finding, Attack Surface, and Environmental. Each group contains multiple metrics, also called factors, that are used to compute a CWSS score (Figure 1):
- The base Finding metric group identifies the inherent risk of the weakness, confidence in the accuracy of the finding, and strength of controls.
- The attack surface metric group includes the barriers an attacker must overcome to exploit the weakness.
- The environmental metric group includes the characteristics of the weakness that relate to a specific environment or operational context.
The following are three of the most common issues found when manually managing memory in code (along with the associated CWE reference).
Use after free
CWE-416 — if the program attempts to access memory that has been freed, it can cause the program to crash or cause unexpected program behavior. UAF can affect integrity by corrupting valid data, causing program crashes through corrupt data, and allowing an attacker to launch malicious code.
Heap-based buffer overflow
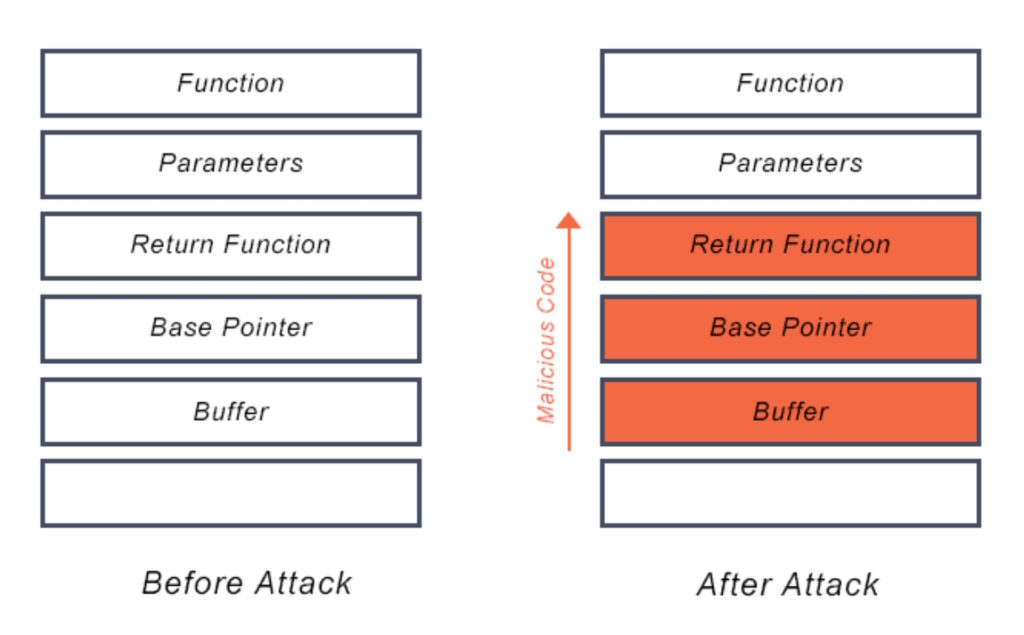
CWE-122 — a heap overflow condition is a buffer overflow, where the buffer that can be overwritten is allocated in the heap portion of memory. Heap-based attacks are more difficult to implement than the stack-based approach but can have more serious consequences. It involves the attack flooding a program’s memory space beyond the memory it uses for current runtime operations. A buffer overflow bug can leave a system vulnerable to attackers who can exploit it by injecting malicious code that can run unauthorized programs or give the attacker administrator access and control of the system (Figure 2).
Missing release of memory after effective lifetime
CWE-401 — missing Release of Memory after Effective Lifetime is also called missing free (MSF). The program has allocated heap memory but failed to free that piece of memory. If the program doesn’t free the memory, it can lead to memory leaks. If the process runs long enough, memory leaks can lead to core dumps or low memory conditions, making the system vulnerable to denial of service (DoS) attacks.
CHERI
The CHERI architecture extensions were designed by the University of Cambridge and SRI International and extend the CPU instruction set to enable it to access memory using capabilities that access specific areas of memory instead of machine-word pointers. Using capabilities provides fine-grained and hardware-enforced access protection. When used with C and C++, CHERI can address memory safety issues without adding the overhead of software runtime checks.
The implementation of CHERI requires minimal changes to existing C and C++ programs. CHERI also enables developers to create separate compartments within a process that can be used to further harden the system against attack. Compartments subdivide applications into sections that can interact only in very controlled manners. For example, sensitive subroutines or systems can be separated from the rest of the application, reducing the opportunities for exploitation.
Summary
Security is an important aspect of memory management in IoT devices. The CWE scheme provides a framework for identifying potential memory management problems and quantifying their severity. The CWE website includes an extensive list of common security weaknesses. The CHERI architecture extensions have been developed to speed the implementation of secure C and C++ code.
References
An Introduction to CHERI, University of Cambridge
Automating and Scaling Vex Generation, Open Source Vulnerabilities
Common Weakness Enumeration, MITRE
Common Weakness Scoring System, MITRE
ISO/IEC TR 20004:2015, Refining software vulnerability analysis under ISO/IEC 15408 and ISO/IEC 18045, ISO
Memory Management Strategies for an Internet of Things System, IEEE International Symposium on Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering
SBOMs and Memory Safety, IoT Security Foundation
Vulnerability Assessment of Sensor Systems, MDPI sensors



Leave a Reply