In the first part of this two-part series, we focus on Wi-Fi HaLow technology. Part two will explore who the major players are and discuss the future of the technology.
What is HaLow?
In 2017 the wireless networking standard IEEE 802.11ah, also called Wi-Fi HaLow (pronounced “HAY-Low”), was released. HaLow uses the 900 MHz industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) unlicensed bands to extend the Wi-Fi range. The Wi-Fi Alliance supports the HaLow standard.
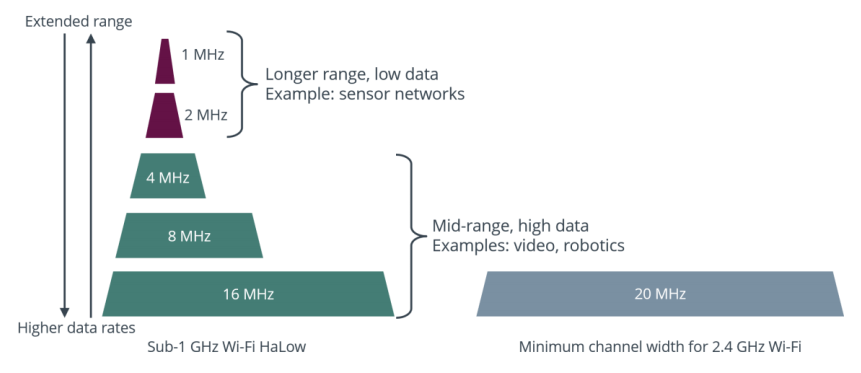
The Wi-Fi (802.11 a/b/g/n) range most people are familiar with operates at either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz. At these frequencies, the radio waves do not travel as far as waves at the lower frequencies do. At 2.4 GHz, the waves can travel less than 259 m (820 feet). LPWAN can typically reach between 1 km to 10 km. In addition, obstacles like walls and doors within a building can block higher-frequency waves (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz). As shown in Figure 1, the Wi-Fi HaLow operating range spans 1 MHz to 16 MHz channels. The 1 MHz channel waves travel farther, while the 16 MHz channel provides higher data transmission rates. A top speed of 80 Mbps can be achieved using the 16 MHz channel.
“Wi-Fi HaLow is well suited to meet the unique needs of the Smart Home, Smart City, and industrial markets because of its ability to operate using very low power, penetrate through walls, and operate at significantly longer ranges than Wi-Fi today. Wi-Fi HaLow expands the unmatched versatility of Wi-Fi to enable applications from small, battery-operated wearable devices to large-scale industrial facility deployments – and everything in between. Wi-Fi HaLow will broadly adopt existing Wi-Fi protocols and deliver many of the benefits that consumers have come to expect from Wi-Fi today, including multi-vendor interoperability, strong government-grade security, and easy setup,” commented Kevin Robinson, Senior Vice President, Marketing of Wi-Fi Alliance.
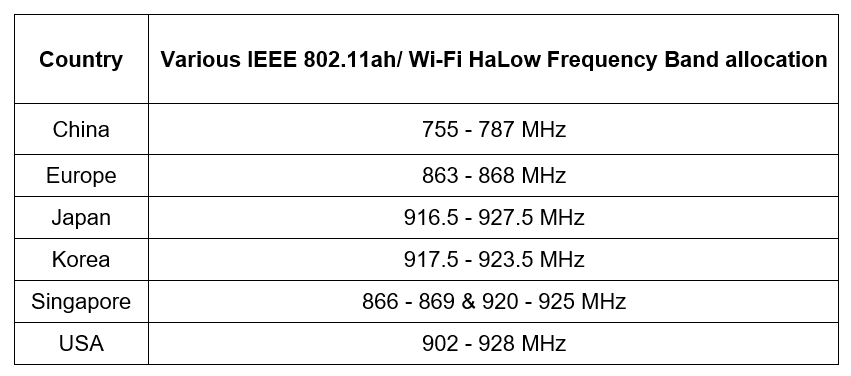
The IEEE 802.11ah/ Wi-Fi HaLow frequency band allocation differs by region. Therefore, devices that work in one region may not be compatible with devices in a region that uses a different frequency band allocation (Figure 2).
What are the applications for HaLow?
IoT use in smart factories, buildings, cities, warehouses, transportation, medical, and many other remote monitoring applications has created significant market opportunities. As a result, the IoT is growing exponentially. However, operating at 2.4 and 5 GHz, today’s Wi-Fi will never solve the IoT problems because it supports a short range of a few hundred meters. IoT connections require distance in the kilometer range. (See answer 1 above). HaLow aims to provide a Wi-Fi IoT solution for applications including smart home, smart city, connected vehicles, agriculture, digital healthcare, and various industrial automation uses, which has not been possible before with the 2.4 GHz /5 GHz Wi-Fi solutions.
HaLow will serve the IoT segments, while traditional Wi-Fi will support high-speed applications, including video streaming. In other words, you will not be able to watch videos using HaLow.
How fast is HaLow?
HaLow’s data rate is scalable; 80 Mbps at 1m and 150 kbps at 1km.
What is the distance range of HaLow?
It can reach a distance of 1km.
Is HaLow a low-power wide area network (LPWAN)?
Yes. Similar to other LPWAN designs and applications, HaLow connects to sensors that transmit data infrequently. Power is only on for a short duration during connection to achieve low power consumption.
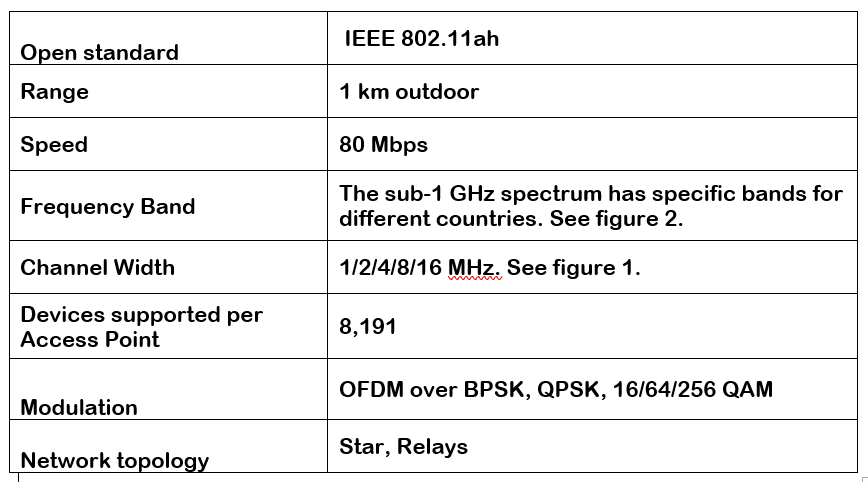
What are the characteristics of the IEEE 802.11ah (HaLow) protocol?
The chart below details HaLow’s specific characteristics.




Leave a Reply