Artificial intelligence (AI) is the field in computer science where machines attempt to mimic human reasoning to recognize and analyze situations and make decisions. AI has been under development for decades, but only recently has computing power and memory become high enough in performance and low enough in cost to make AI a practical tool in selected applications. Even with that, however, there is still a tremendous need to make AI more efficient, more flexible, and lower in cost.
AI is computationally complex and is based on huge numbers of arithmetic operations. GPUs are often used to implement AI systems. While CPUs contain several complex cores, GPUs can contain hundreds of simple cores optimized to perform specific operations, and the cores in a GPU can operate in parallel, shrinking the time it takes to complete intensive computations.
GPUs have their own limitations: GPUs have limited on-chip cache memories, and AI consumes large quantities of data. That means that the bulk of the data has to be stored off-chip with lots of data movement into and out of the GPU. That slows the overall operation. And GPUs are limited in the operations that they can perform and must be used in combination with a CPU for handling general tasks. FPGAs can offer an alternative to GPUs. Regardless of whether GPUs, FPGAs, or even CPUs are employed, a hardware platform called an AI accelerator is typically used to implement AI applications such as neural networks, machine vision, and machine learning in servers.
For example, the Alveo U250 AI accelerator from Xilinx uses an FPGA to increase real-time inference throughput by 20X versus high-end CPUs, and more than 4X for sub-two-millisecond low-latency applications versus fixed-function accelerators like high-end GPUs. Moreover, Alveo accelerator cards reduce latency by 3X versus GPUs, providing a significant advantage when running real-time inference applications.

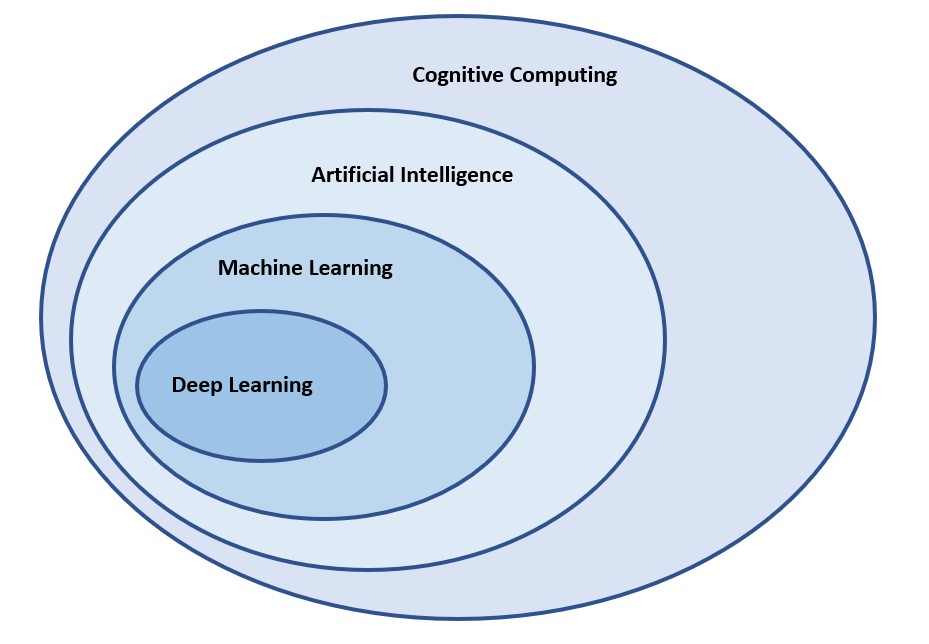
AI is not a monolithic technology. There are various subsets of AI. Machine learning (ML), for example, uses training algorithms to determine the most likely outcome of a limited set of situations. Deep learning enables the system to be self-training to learn how to perform specific tasks. And AI itself is part of a larger area called cognitive computing.
Machine learning and pruning
In ML, pruning means simplifying, compressing, and optimizing a decision tree by removing sections that are uncritical or redundant. Pruning attempts to limit “overfitting” in decision trees created through ML. “Overfitting” refers to the unnecessary expansion of a decision tree by the inclusion of incorrect attribute values or class membership, which can contaminate data sets. Through pruning, the unnecessary and incorrect branches are shortened or eliminated.
Pruning is also important when implementing ML on mobile devices of the Internet of Things nodes where computing power is limited. Optimally, pruning reduces the size of a decision tree without reducing the predictive accuracy. Various techniques for decision tree pruning exist that differ in the measurement that is used to optimize performance.
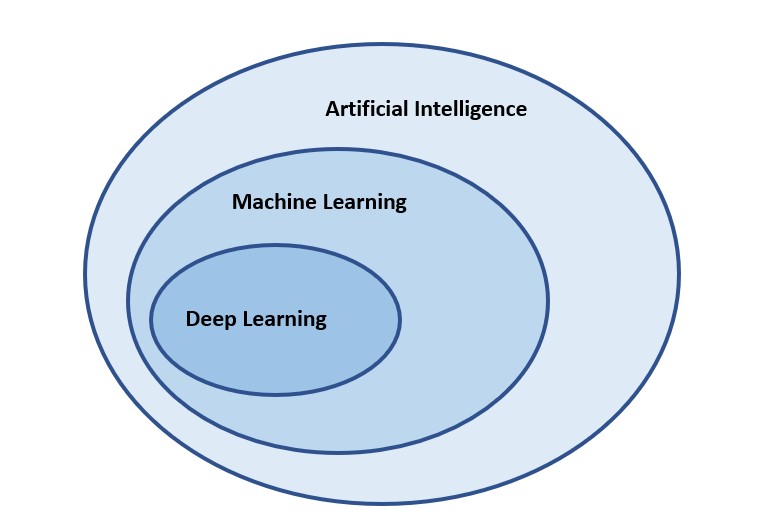
Figure 2: Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning, which in turn is a subset of artificial intelligence. (Image: Jeff Shepard)
Deep learning
Like AI in general, Deep learning, also called deep structured learning, involves two phases. The first is the training phase in which the inference algorithm is fine-tuned to produce the required level of accuracy and repeatability. The second phase is the use phase, where the training data is used to provide an acceptable range of outcomes.
The adjective “deep” in deep learning comes from the use of multiple layers in the network. In deep learning, the layers are permitted to be “structured” and heterogeneous, for the sake of efficiency and trainability.
Deep learning is often associated with machine perception, such as image and speech recognition. It uses multiple layers to extract higher-level features from the raw input progressively. For example, in image processing, lower layers may identify general physical characteristics such as colors, textures, edges, and so on. In comparison, higher layers may identify more detailed elements as numbers, letters, or faces.
Cognitive computing and machine perception
Cognitive computing refers to systems that interact naturally with humans by using a combination of large scale learning, reasoning, and environmental perception. It is a mixture of AI and cognitive/behavioral science.
Cognitive computing is a step beyond AI. AI is focused on deriving accurate results for specific learned situations. Cognitive computing is focused on mimicking human behavior in unstructured situations, adapting human reasoning, and solving complex problems in ways similar to those used by humans. For example, natural language processing for cognitive computing goes beyond simple voice recognition. It includes being able to sense an individual’s mood (stress, anger, happiness, frustration, excitement) and modify responses accordingly.
AI is a fast-changing and complex field. Until recently, there were no performance benchmarks for AI or ML systems. That is changing. Today, several industry organizations have developed AI and ML benchmarks, with more complex benchmarks under development. The second FAQ in this series will review the current status of AI and ML performance benchmarks and look into what new performance benchmarks may be appearing in the near future.
References
Cognitive computing definition, Cognitive Computing Consortium
Machine learning, Wikipedia
What is pruning in machine learning?, Neural Magic




Leave a Reply