The COM Express open standard, initially released in 2005, covers Computer on Modules (CO) and Single Board Computers (SBCs) under the auspices of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturer’s Group (PICMG), a consortium of equipment and system vendors, component suppliers, and end users for the embedded computer market. Open standards are not open source, but they […]
FAQ
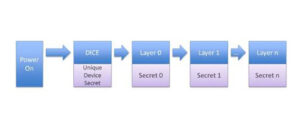
What is DICE architecture?
DICE stands for Device Identifier Composition Engine, and it is a security standard created by the Trusted Computing Group (TCG) which has been addressing security issues for years. TCG announced the establishment of DICE Architecture, or DICE Architecture Work Group to address the need for increased security in the Internet of Things (IoT) therefore targeting […]
SSDs vs. HDDs Part 2: Sand or Rust?
Solid State Drives (SSDs) are faster, more rugged, and (presently) more expensive than Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). When SSDs are priced competitively to HDDs, we will begin to see every PC equipped with an SSD for long-term storage, because SSDs are suitable for a decade or more of typical consumer use. SSD is just Flash […]
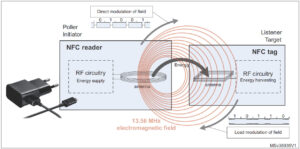
NFC Tag Basics: How to use for programming automation
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a wireless communication technology that acts over short distances for two-way communication. The use of NFC tags is growing in several markets, including the medical, consumer, retail, industrial, automotive, and smart grid markets. NFC is a type of Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. When two NFC enabled devices are very close […]
What are MRAMs?
MRAM, Magneto-Resistive Random Access Memory, is a type of non-volatile memory (NVM) capable of holding saved data even if the power is down or the power is accidentally cut off. MRAM — also called Magnetic RAM — is not new. It has been in the market for more than two decades, but there have been several […]
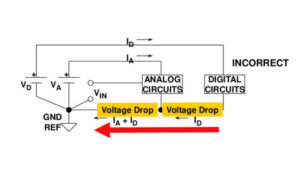
Built-in analog-to-digital converters
There are sensors for a plethora of smart applications that can measure a wide range of parameters (e.g., temperature, light, acceleration, pressure, proximity, etc.). The real world data is analog. Therefore sensors typically provide analog data in the form of voltage (e.g., 0V-5V) and most of the time this data is later transformed into digital […]
PCB layout guidelines and considerations
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) layout, in its most basic form, is a means to transfer a circuit from a breadboard to a more stable and permanent physical form. Whereas entire books and college coursework have been dedicated to PCB layout, what follows is a short overview of what to consider when making a PCB. […]
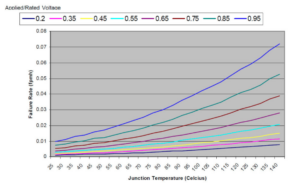
Calculating fudge factor (or electronic component de-rating)
Adding a “fudge factor” is actually a thing in engineering, but there’s a more formal-sounding name for it: de-rating. Both refer to the process of providing more robustness than is called for. There are many reasons for doing this. Sometimes new components are on the low side of average. For instance, electronics components are rated […]
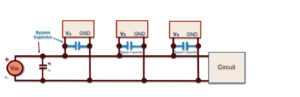
Decoupling capacitor or bypass capacitors: why so many?
A capacitor behaves like an open circuit at DC voltages. (Recall that DC is voltage that operates at a frequency of 0 Hz, which is a flat-line voltage of varying heights or levels). If there’s an AC (varying) component or noise in the signals traveling in the circuit, then as the frequencies of the varying […]
Core independent peripherals have zero dependence on CPUs…really?
The Core Independent Peripheral (CIP) is a term coined by Microchip Technology to describe an unusual control scheme whereby peripherals do not rely upon input from the Central Processing Unit (CPU). Microchip claims that these self-sustaining peripherals free up the CPU, increase power savings, reduce development time and are easily configured with Microchip graphical programming […]