The basics of microcontroller units (MCUs) and microprocessor units (MPUs) haven’t changed too much. But application requirements have. What was once a simple automotive, industrial, or medical control system may now include edge AI processing, increasingly demanding security requirements, or complex 3D animated human machine interfaces (HMIs). That can change the game when choosing between […]
FAQ
FAQ on Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM)
There are many non-volatile memory technologies in use; RRAM is another option — maybe. Random access memory (RAM), sometimes called by a more descriptive name of read/write (R/W) memory, is critical to modern electronic systems. Small amounts are needed as a numeric scratchpad or to store data samples before processing; moderate amounts are needed to […]
Can chiplets save the semiconductor supply chain?
We’re making more semiconductors than ever before, and yet somehow, it’s still not enough. Demand is continuously increasing, spurred by the rise of AI in our everyday lives, but production still faces bottlenecks. The problem is more than just scale; it comes down to the structure of the manufacturing industry as a whole. As of […]
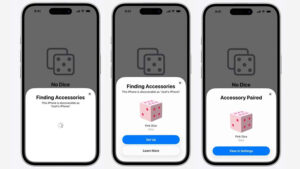
Why is the Matter 1.4.2 update important?
Matter 1.4.2 is a maintenance release that improves security, streamlines certification, and optimizes infrastructure operation. This article presents only highlights. In addition to improving certain areas of performance, it adds more new features than most maintenance releases. And, like most maintenance releases, it addresses issues found in previous versions and fine-tunes operations to improve reliability, […]
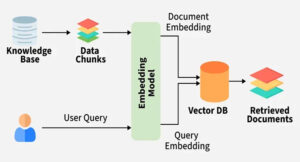
When should you use RAG, TAG, and RAFT AI?
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and table-augmented generation (TAG) are both techniques to improve the ability of artificial intelligence (AI) to generate accurate and relevant information by leveraging external data. Other choices include retrieval-augmented fine-tuning (RAFT) and retrieval-centric generation (RCG). Understanding when to use RAG, TAG, RAFT, and RCG can be crucial to successful and efficient AI […]
What is JESD209-6 and why is it important for edge AI?
JESD209-6, the recently released LPDDR6 (low power double data rate 6) standard by JEDEC, represents a significant leap forward in memory technology, particularly for devices with limited power budgets. It’s crucial for the next generation of mobile devices, AI applications, and edge computing, where high performance and power efficiency are paramount. It’s also expected to […]
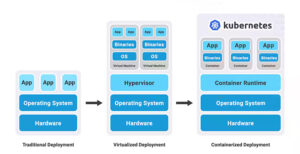
What kinds of tools are available for optimizing edge AI performance?
Developers can turn to model optimization frameworks and libraries, model optimization, distillation, and compression tools, plus hardware-specific optimization tools and development platforms for optimizing edge AI performance. Kubernetes and containerization provide additional tools for optimizing AI edge performance. Frameworks and libraries are collections of pre-written code. Libraries are collections of components, classes, and methods that […]
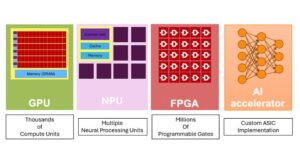
What are the hardware strategies for building energy-efficient AI accelerators?
Artificial intelligence (AI) applications are spreading to more industries every day. However, the amount of energy used by these AI systems has become a significant issue. Modern deep neural networks require a considerable amount of computing power. This article examines five key hardware strategies for building energy-efficient AI acceleration: dedicated accelerator architectures, analog in-memory computing, […]
How to select and place antennas in IoT devices
Impacting range and performance, antenna selection and placement are key design considerations for Internet of Things (IoT) device manufacturers. This article reviews the most widely used IoT antennas and discusses their application-specific functions. It also highlights optimal design and placement strategies, offering detailed guidelines for each antenna type. Range and frequency requirements Range and frequency […]
How can silent data corruption be detected and corrected in AI systems?
Silent data corruption (SDC), sometimes called bit rot or silent data errors (SDEs), refers to errors in data that are not detected by standard error-checking mechanisms, leading to potentially significant data loss or incorrect calculations. SDCs can lead to inaccurate training, incorrect predictions, and unreliable performance. Detecting SDC requires specialized techniques and tools. SDCs can […]