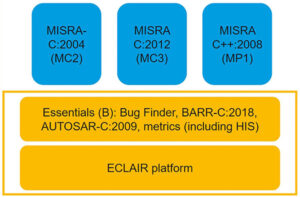
MISRA is a set of C and C++ coding standards developed by the Motor Industry Software Reliability Association (MISRA). Today it’s being maintained and expanded by the MISRA Consortium. MISRA has grown into a standard for embedded industries as well as automotive systems. For example, ISO 26262 Functional Safety – Road Vehicles cites MISRA C […]
FAQ
Why 3D packaging could be the next breakthrough for processing
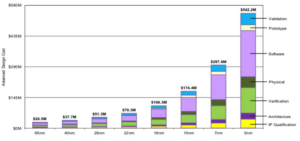
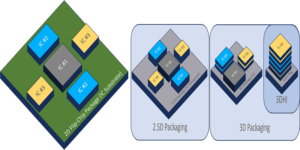
By Brian Hendren, Tektronix As semiconductor manufacturers start to reach the potential physical limits of shrinking process nodes, chip packaging is emerging to improve performance. Flip chip assembly remains the most popular method for interconnecting dies, but new advancements in silicon interposers are enabling 2.5D packaging architectures and, in turn, making 3D packaging possible. To […]
Why advanced packaging is vital to the future of semiconductors
The cost and the physics of fitting more transistors in the space available are showing diminishing returns. The concept of “known good die” is much more difficult to quantify. For all the talk in the semiconductor industry about trying to reach 1.8 nm process nodes, advanced packaging and its impact on performance seems to be […]
Post-quantum crypto standardization — background
At some point in the not-too-distant future, it’s expected that quantum computing will pose a security risk to all currently used encryption techniques. Most current encryption methods are based on the challenges associated with factoring large numbers into their prime factors. They provide good levels of security when classical computers are being used. Still, quantum […]
Post-quantum crypto standardization — what’s the end game?
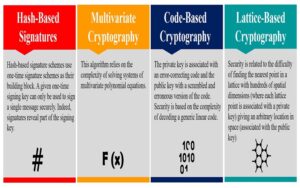
The post-quantum cryptography (PQC) standardization program being run by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is developing encryption algorithms to protect classical computers from attacks by quantum computers. NIST has announced the first four PQC algorithms and is preparing them for final development. In the meantime, organizations of all types are analyzing the […]
What’s a quantum processing unit?
Quantum processing units (QPUs) are the quantum equivalent of microcontrollers (MCUs) in electronic equipment. QPUs and the quantum computers that use them are evolving and heading toward large-scale computing. This FAQ looks at current quantum computing architectures and how they are evolving and reviews currently available QPUs and efforts to develop QPUs based on superconductivity […]
IoT: Microcontrollers and sensors must work as a team
Get an understanding of how to select sensors and microcontrollers for your IoT product, with an emphasis on circuit design to optimize performance. Sensors in IoT devices collect data from the environment, after which the data can be processed and analyzed to make intelligent decisions. The quality of your sensors and how well you integrate […]
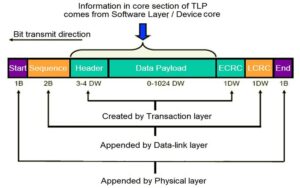
How does the PCIe protocol stack work?
The Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard. It’s the common motherboard interface in systems from personal computers to servers and storage devices and is used with graphics cards, sound cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet hardware connections. It uses a three-layer protocol stack to […]
What are the five types of quantum computers?
There are several ways to make the quantum bits (qubits) that comprise quantum computers. The classic image of the “chandelier” descending into a cryostat only represents qubits that need to operate near 0 Kelvin (K). They are used by IBM, Google, and others, but those pictures present a very limited view of quantum computing. This […]
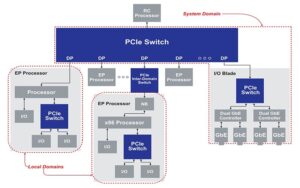
What’s a PCIe root complex?
The root complex in PCI Express (PCIe) is the intermediary between the system’s central processing unit (CPU), memory, and the PCIe switch fabric that includes one or more PCIe or PCI devices. It uses the link training and status state machine (LTSSM) to manage connected PCIe devices. The LTSSM detects, polls, configures, recovers, resets, and […]