When designing a new system, you might find yourself drawn to a new processor with features that can make a real difference in the final product. Most semiconductor vendors will provide an evaluation board that you can use to evaluate whether or not you want to invest your time and money into that particular processor […]
FAQ
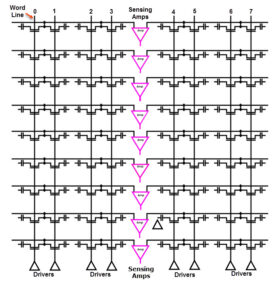
What is DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) vs SRAM?
Both DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) and SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) are types of Random Access Memory (RAM). RAM is a semiconductor device internal to the integrated chip that stores the processor that a microcontroller or other processor will use constantly to store variables used in operations while performing calculations. RAM refers to the […]
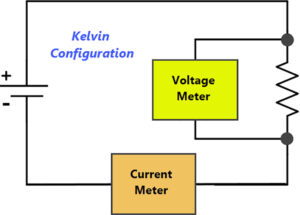
Accurately measure power consumption with Kelvin configuration
How do you accurately measure power consumption when the leads of your multimeter add resistance to your measurement? How do you accurately measure the resistance of a device that’s low, (e.g., less than 10 ohms) when the leads of your multimeter add resistance? One way to get a more accurate reading is to use the […]
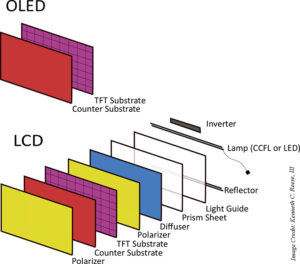
Display options for MCUs: LCD, LED, and OLED
Microcontrollers (MCUs) have a few display options available. A Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is a common, low-cost option that uses a backlight made of either cold-cathode fluorescent tubes (CCFL) or light emitting Diodes (LEDs). The term “LED display” actually refers to an LCD display with LED backlighting, and thus is the same thing as an […]
GPUs: Not just for graphics anymore
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) are special processors that can rapidly process repetitive computations. GPUs were originally designed for rendering performance-hungry display graphics to take excess load off of CPUs. GPUs can be characterized by extremely fast computing power, especially in repetitive computations. Within the past decade, GPUs are increasingly used in applications that require […]
RISC architecture and instruction architecture
RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computer and is a type of architectural processor design strategy. “Architecture” refers to the way a processor is planned and built and can refer to either the hardware or the software that is closest to the silicon on which it runs. An Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) specifies the basic […]
Documenting code: use this when you just don’t know what to write
Documenting code is something most people dislike doing. By the time you are done with writing, debugging, testing, fixing and re-testing, you are so sick of it that you just don’t want to look at it anymore. But most of us have already been on the other side of the code: a recipient of some […]
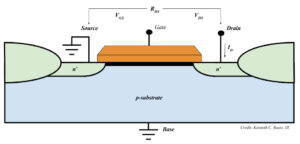
Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistor: What is RDS(on)?
RDS(on) stands for “drain-source on resistance,” or the total resistance between the drain and source in a Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistor, or MOSFET when the MOSFET is “on.” RDS(on) is the basis for a maximum current rating of the MOSFET and is also associated with current loss. All things being equal, the lower the […]
RF cable and RF wireless transmission
What is RF? RF stands for “Radio Frequency” and has become a catch-all term for certain wired communications and a large (spectral) range of wirelessly transmitted waves. It’s easy to find wireless RF modules for microcontroller development kits and other design-ready products, but where does RF cable fit in? What does Ethernet have to do […]
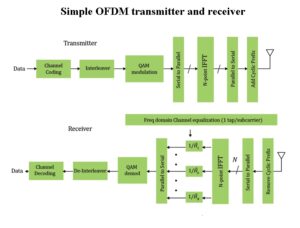
Modulating 5G
The IoT will make heavy use of fifth-generation mobile networks that use a yet-to-be-determined modulation scheme. Here are the major contenders. LEE TESCHLER | EXECUTIVE EDITOR Fifth-generation mobile networks, abbreviated 5G, will form the telecommunications standards for the internet of things. Planners say 5G will have a higher capacity than the current 4G equipment partly […]