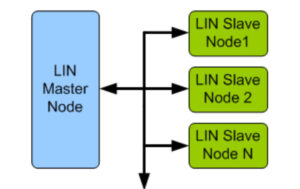
The local interconnect network (LIN) bus is a single-wire bus (using the chassis ground) that enables the inexpensive integration of sensors and actuators in automobile networks. It can be used to create small subnets and can communicate over a power distribution system with a DC-LIN transceiver. This FAQ reviews the basics of LIN networks, details […]
What are basic logic gates?
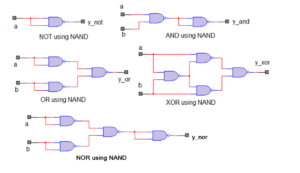
Logic gates are the building blocks of digital circuits. The basic logic gates include AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR. They can be implemented in digital hardware using transistors and/or diodes. In a few applications, they are implemented using electromechanical relays, fluidics, pneumatics, or optical elements. A series of logic gates can be […]
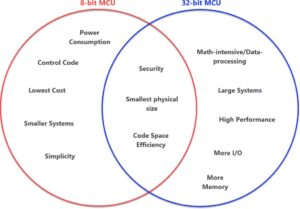
Security standards and MCUs
Security is an important concern for developers of all types of systems. This FAQ reviews several important security standards for IoT cyber security, security vulnerabilities in industrial automation and control systems, standards for analyzing and identifying secure coding errors in C applications, and concepts of application software security and levels of trust. The European Telecommunications […]
What’s a Neural microcontroller?
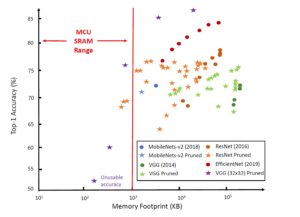
The ability to run neural networks (NNs) on MCUs is becoming increasingly important to support artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in the Internet of Things (IoT) nodes and other embedded edge applications. Unfortunately, running NNs on MCUs is challenging due to the relatively small memory capacities of most MCUs. This article details the […]
What happens when an MCU powers up?
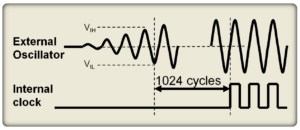
MCU start up is a highly structured process designed to ensure proper operation. Numerous elements are involved including initial power/voltage sequencing and regulation, oscillator startup, the use of a vector table, boot loaders (including possible secure boot), and application initialization. This FAQ walks step-by-step through the various elements involved during the start-up of an MCU. […]
MCU Bits and Bytes: sizes, types, and uses
Bits are the 1s and 0s that form the basis of digital information. A group of 8 bits is a byte and forms the basis of digital computing. Bits and bytes are used for storing and processing information as well as other functions in a digital IC. This FAQ begins with a brief review of […]
How to extend, boost and repeat Wi-Fi signals
Since the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) limits Wi-Fi transmitter power, it’s often necessary to increase the range of Wi-Fi signals using some signal boosting/extending technology. But transmit power is only half of the equation. Wi-Fi connections are always bidirectional and symmetrical. When working to extend Wi-Fi signals, the bidirectional nature of the connection is […]
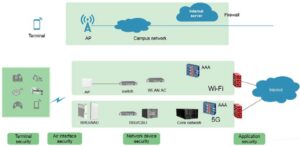
The basics of Wi-Fi security and encryption
Wi-Fi security has significantly improved over the years from initially being more aspirational than real until today, where Wi-Fi 6 security is considered to be on a par with the security of 5G telephony. This FAQ will answer several questions related to Wi-Fi security and encryption: What’s the difference between WEP, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3? […]
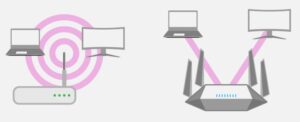
What to consider when selecting a Wi-Fi antenna
Antennas are a critical part of the link budget in all wireless communications applications, including Wi-Fi. In addition to the numerous antenna performance and link budget issues in wireless communications, there are general architectural challenges. The architectural options are the focus of this FAQ, including; long-distance versus local Wi-Fi and the use of directional vs. […]
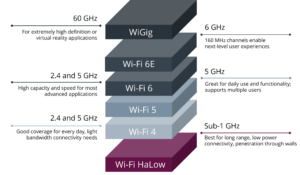
Wi-Fi by the numbers
This FAQ briefly reviews the generations of Wi-Fi and backward compatibilities, looks at the different frequency bands used by the latest Wi-Fi specifications, and reviews the bandwidths offered by various Wi-Fi implementations. The first five generations of Wi-Fi focused on evolutionary and incremental advancements and backward compatibility. Wi-Fi 6 changed that trajectory and is a […]