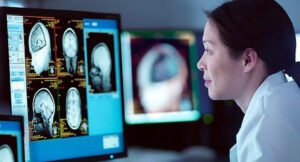
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) are powerful and flexible devices. They combine the performance of custom designs with reprogrammability, even after the system is in the field. As a result, FPGAs are increasingly used in various systems, from the Mars rover to fighter jets and from communications and automotive systems to a growing variety of […]
FPGAs and other programmable devices – what’s the difference?
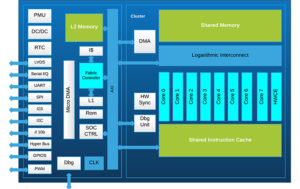
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) are digital ICs consisting of arrays of logic blocks that can be programmed (wired) and reprogrammed multiple times, even after the product containing the FPGA has been shipped and is “in the field.” FPGAs are not a monolithic technology; there are variations in how FPGAs are structured and programmed, variations […]
RISC-V for ultra-low power processing and AI on the edge
RISC-V is an exciting and rapidly-emerging technology. RISC-V is software; it is an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA) based on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. So far, this FAQ series has looked at how “RISC-V is growing and offers stability, scalability, and security,” the “Growing availability of tools reducing the risk of […]
RISC-V for artificial intelligence machine learning and embedded systems
Several RISC-V development efforts are targeting applications such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and other high-performance embedded applications. The previous two FAQs in this series considered the capabilities of RISC-V and the near-term risks associated with the technology, and the growing availability of tools that are helping to reduce the […]
Growing availability of tools reducing risk of using RISC-V
As discussed at the end of the first FAQ in this series, “RISC-V is growing and offers stability, scalability, and security,” there is a lack of testing standards and tools for RISC-V compared with mature ISAs such as Intel and Arm. This is an area that is experiencing accelerating developments and progress. The growing availability […]
RISC-V is growing and offers stability, scalability and security
RISC-V is growing rapidly. Semico Research has projected that 62.4 billion RISC-V CPU cores will be sold in 2025. While that’s only about 6% of the overall CPU core market, RISC-V is an emerging technology that most designers should follow and become increasingly familiar with. RISC-V is becoming more commercially attractive as a result of […]
Quantum compasses and optical imaging for global positioning and navigation
There is an emerging demand for a replacement for today’s global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), and especially for the global position system (GPS) in the U.S. Part one of this three-part FAQ series presented several of the shortcomings of today’s GPS technology and some efforts to augment it and improve its performance. Part two presented […]
eLORAN a terrestrial alternative to GPS
Terrestrial-based hyperbolic navigation technologies predate today’s satellite-based global positioning system (GPS). Starting with developments in the 1930s and 1940s, land-based long-range navigation (LORAN) systems using hyperbolic navigation have been continuously advanced. Today, the enhanced LORAN (eLORAN) system has been offered a more secure alternative to GPS. Hyperbolic navigation technologies were independently developed in the U.S. […]
GPS is a ubiquitous and problematic technology
Much of the world depends upon satellite systems for precise navigation and timing services. The global positioning system (GPS) is a ubiquitous and problematic technology. Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is the umbrella term for satellite navigation systems that provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning with global coverage. GNSS includes GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, Beidou, and other regional […]
Functional safety for embedded systems – Virtual Roundtable (part 2 of 2)
Hosted by Jeff Shepard, EE World has organized this “virtual roundtable” into “Functional Safety for Embedded Systems.” Panelists include Anders Holmberg (AH), General Manager Embedded Development Tools with IAR Systems, Mike Dow (MD), Senior Product Manager, IoT Security with Silicon Labs, Jim McElroy (JM), VP of sales and marketing at LDRA Technology, Dave Hughes (DH), […]